第十四章:compiler 编译器 - 深入编辑器处理逻辑
01:前言
上一章中,我们处理了基础的编辑器。但是针对于一些复杂的场景:
- 响应性数据
- 多个子节点
- 指令
我们还没有办法进行对应的处理。
那么对于本章,我们将会深入编辑器,来了解更加复杂的编辑处理。
因为我们前面已经查看多很多的 vue 源码逻辑,所以对于本章而言,我们不会再从基础的源码逻辑进行跟踪查看,而是 仅针对当前场景,查看复杂部分的差异性处理,以此来让我们的整体节奏,变得更加清晰。
那么明确好了以上问题之后,下面就让我们进入到本章的学习吧。
02:响应性数据的编辑器处理:响应性数据的处理逻辑
那么首先我们先来看响应性数据的编辑器处理逻辑。他具体指的是什么呢?我们来看如下测试实例 packages/vue/examples/compiler/compiler-rective.html :
<script>
const { compile, h, render } = Vue
// 创建 template
const template = `<div> hello {{ msg }} </div>`
// 生成 render 函数
const renderFn = compile(template)
// 创建组件
const component = {
data() {
return {
msg: 'world'
}
},
render: renderFn
}
// 通过 h 函数,生成 vnode
const vnode = h(component)
// 通过 render 函数渲染组件
render(vnode, document.querySelector('#app'))
</script>在以上代码中,我们通过 data 声明了一个响应式数据,然后在 tempalte 中通过 进行使用使用。从而得到了 hello 这样一个表达式,这样的表达式我们把它叫做 复合表达式
我们可以在 vue 的源码的 baseCompile 方法中分别查看 AST 、JavaScript AST 和 render 函数的值:
// AST
{
"type": 0,
"children": [
{
"type": 1,
"tag": "div",
"tagType": 0,
"props": [],
"children": [
{
"type": 2,
"content": " hello ",
"loc": {}
},
{
"type": 5, // NodeTypes.INTERPOLATION
"content": {
"type": 4, // NodeTypes.SIMPLE_EXPRESSION
"isStatic": false,
"constType": 0,
"content": "msg",
"loc": {}
},
"loc": {}
}
],
"loc": {}
}
],
...
}// JavaScript AST
{
"type": 0,
"children": [
{
"type": 1,
"ns": 0,
"tag": "div",
"tagType": 0,
"props": [],
"isSelfClosing": false,
"children": [
{
"type": 8,
"loc": {},
"children": [
{
"type": 2,
"content": " hello ",
"loc": {}
},
" + ",
{
"type": 5, // NodeTypes.INTERPOLATION
"content": {
"type": 4, // NodeTypes.SIMPLE_EXPRESSION
"isStatic": false,
"constType": 0,
"content": "msg",
"loc": {}
},
"loc": {}
}
]
}
],
"loc": {},
"codegenNode": {...},
"loc": {}
}
}
],
"helpers": [Symbol("openBlock"), Symbol("createElementBlock"), Symbol("toDisplayString")],
"codegenNode": {...},
"loc": {}
},
"loc": {}
}// context.code
const _Vue = Vue
return function render(_ctx, _cache) {
with (_ctx) {
const { toDisplayString: _toDisplayString, openBlock: _openBlock, createElementBlock: _createElementBlock } = _Vue
return (_openBlock(), _createElementBlock("div", null, " hello " + _toDisplayString(msg), 1 /* TEXT */))
}
}由以上内容可以看出,当我们增加了复合表达式之后,AST、JavaScript AST 和 render 函数中多出了如下内容:
// AST
{
"type": 5, // NodeTypes.INTERPOLATION
"content": {
"type": 4, // NodeTypes.SIMPLE_EXPRESSION
"isStatic": false,
"constType": 0,
"content": "msg",
"loc": {}
}
}// JavaScript AST
{
"type": 8,
"loc": {},
"children": [
{
"type": 2,
"content": " hello ",
"loc": {}
},
" + ",
{
"type": 5, // NodeTypes.INTERPOLATION
"content": {
"type": 4, // NodeTypes.SIMPLE_EXPRESSION
"isStatic": false,
"constType": 0,
"content": "msg",
"loc": {}
},
"loc": {}
}
]
}// render
const _Vue = Vue
return function render(_ctx, _cache) {
+ with (_ctx) {
+ const { toDisplayString: _toDisplayString, openBlock: _openBlock, createElementBlock: _createElementBlock } = _Vue
+ return (_openBlock(), _createElementBlock("div", null, " hello " + _toDisplayString(msg), 1 /* TEXT */))
+ }
}那么当我们处理复合表达式的编译时,同样也是需要从差异入手,我们 只需要填充对应的数据差异,就可以完成最终 render 的生成。
03:响应性数据的编辑器处理:AST 解析逻辑
// 需要新增的 AST 结构
{
"type": 5, // NodeTypes.INTERPOLATION
"content": {
"type": 4, // NodeTypes.SIMPLE_EXPRESSION
"isStatic": false,
"constType": 0,
"content": "msg",
"loc": {}
}
}查看 packages/compiler-core/src/parse.ts 中的代码逻辑,找到 parseChildren 方法。
我们知道该方法的主要是用来解析子节点,内部存在如下的 if 逻辑:
if (startsWith(s, '{{')) {
...
}对于该逻辑而言,它就是用来处理复合表达式的对应逻辑,我们可以在该逻辑中,生成对应的 node:
function parseChildren(context: ParserContext, ancestors) {
...
while (!isEnd(context, ancestors)) {
...
if (startsWith(s, '{{')) {
+ node = parseInterpolation(context)
}
// < 意味着一个标签的开始
else if (s[0] === '<') {
...
}
...
return nodes
}然后增加 parseInterpolation 方法:
/**
* 解析插值表达式 {{ xxx }}
*/
function parseInterpolation(context: ParserContext) {
// open = {{
// close = }}
const [open, close] = ['{{', '}}']
advanceBy(context, open.length)
// 获取插值表达式中间的值
const closeIndex = context.source.indexOf(close, open.length)
const preTrimContent = parseTextData(context, closeIndex)
const content = preTrimContent.trim()
advanceBy(context, close.length)
return {
type: NodeTypes.INTERPOLATION,
content: {
type: NodeTypes.SIMPLE_EXPRESSION,
isStatic: false,
content
}
}
}至此,我们成功解析了 AST。
打印解析之后的 AST 可得:
const ast = {
type: 0,
children: [
{
type: 1,
tag: 'div',
tagType: 0,
props: [],
children: [
{ type: 2, content: ' hello ' },
{ type: 5, content: { type: 4, isStatic: false, content: 'msg' } },
{ type: 2, content: ' ' }
]
}
],
loc: {}
}我们可以把以上代码替换到源码的 baseCompile 中,发现可正常渲染。证明我们当前生成的 AST 没有问题。
04:响应性数据的编辑器处理:JavaScript AST 转化逻辑
// 需要新增的 JavaScript AST 结构
{
"type": 8,
"loc": {},
"children": [
{
"type": 2,
"content": " hello ",
"loc": {}
},
" + ",
{
"type": 5, // NodeTypes.INTERPOLATION
"content": {
"type": 4, // NodeTypes.SIMPLE_EXPRESSION
"isStatic": false,
"constType": 0,
"content": "msg",
"loc": {}
},
"loc": {}
}
]
}对于 JavaScript AST 转化逻辑 我们主要需要明确两个地方:
- 加号的拼接
NodeTypes.INTERPOLATION的处理
加号的拼接
加号的拼接,我们之前已经处理过了。
在 packages/compiler-core/src/transforms/transformText.ts 中,我们存在一个 transformText 方法,该方法就可以处理复合表达式,生成对应的加号拼接
NodeTypes.INTERPOLATION
在 vue-next-mini 中的 packages/compiler-core/src/transform.ts 模块下,有一个 traverseNode 方法,该方法可以帮助我们处理节点的转化逻辑。
节点的处理需要额外增加
toDisplayString方法,所以我们需要在packages/compiler-core/src/runtimeHelpers.ts中新增MAP:js... export const TO_DISPLAY_STRING = Symbol('toDisplayString') /** * const {xxx} = Vue * 即:从 Vue 中可以被导出的方法,我们这里统一使用 createVNode */ export const helperNameMap = { // 在 renderer 中,通过 export { createVNode as createElementVNode } ... [TO_DISPLAY_STRING]: 'toDisplayString' }在
packages/compiler-core/src/transform.ts中的traverseNode下,新增NodeTypes.INTERPOLATION处理:jsexport function traverseNode(node, context: TransformContext) { ... // 继续转化子节点 switch (node.type) { ... // 处理插值表达式 {{}} case NodeTypes.INTERPOLATION: context.helper(TO_DISPLAY_STRING) break } ... }
打印此时生成的 JavaScript AST(不要忘记为 helpers 增加 [CREATE_ELEMENT_VNODE, TO_DISPLAY_STRING] ):
{
type: 0,
children: [
{
type: 1,
tag: 'div',
tagType: 0,
props: [],
children: [
{
type: 8,
children: [
{ type: 2, content: ' hello ' },
' + ',
{
type: 5,
content: { type: 4, isStatic: false, content: 'msg' }
},
' + ',
{ type: 2, content: ' ' }
]
}
],
codegenNode: {
type: 13,
tag: '"div"',
props: [],
children: [
{
type: 8,
children: [
{ type: 2, content: ' hello ' },
' + ',
{
type: 5,
content: { type: 4, isStatic: false, content: 'msg' }
},
' + ',
{ type: 2, content: ' ' }
]
}
]
}
}
],
loc: {},
codegenNode: {
type: 13,
tag: '"div"',
props: [],
children: [
{
type: 8,
children: [
{ type: 2, content: ' hello ' },
' + ',
{
type: 5,
content: { type: 4, isStatic: false, content: 'msg' }
},
' + ',
{ type: 2, content: ' ' }
]
}
]
},
helpers: [CREATE_ELEMENT_VNODE, TO_DISPLAY_STRING],
components: [],
directives: [],
imports: [],
hoists: [],
temps: [],
cached: []
}我们可以尝试把该内容放入到 vue 3 源码的 baseCompile 方法中,可以正常渲染。证明 JavaScript AST 渲染完成。
05:响应性数据的编辑器处理:render 转化逻辑分析
// render 函数,内容进行了简化
const _Vue = Vue
return function render(_ctx, _cache) {
+ with (_ctx) {
+ const { toDisplayString: _toDisplayString, createElementBlock: _createElementBlock } = _Vue
+ return _createElementBlock("div", null, " hello " + _toDisplayString(msg)
+ }
}
代码块12345678910那么接下来我们就要处理 render 的转化逻辑了。由以上最终生成的方法可知,对于主要增加了以下两块代码:
toDisplayString方法:该方法的作用非常简单,接收一个变量,返回对应的响应性数据。比如在以上代码和测试场景中,_toDisplayString(msg)方法的调用代表着接收msg变量作为参数,返回world字符串with (_ctx):由刚才的代码我们可知,在使用_toDisplayString时,我们用到了一个msg变量。但是在整个的render代码中却没有msg变量的存在。那么为什么没有抛出对应的错误呢?这是因为 with 的作用,它会改变语句的作用域链,从而找到msg变量。
所以根据以上两点,我们在去处理时,就需要关注以下内容:
- 在
generate方法中,增加with的push和toDisplayString方法的调用 - 完成
toDisplayString方法 - 因为
with改变作用域,所以我们在runtime时,需要注意新的作用域会不会引发其他的错误。
06:响应性数据的编辑器处理:generate 生成 render 函数
这一小节我们来完成 generate 的函数拼接:
在
generate方法中,新增with的处理:jsexport function generate(ast) { ... // 增加 with 触发(加到 hasHelpers 之前) push(`with (_ctx) {`) indent() // 明确使用到的方法。如:createVNode const hasHelpers = ast.helpers.length > 0 ... // with 结尾 deindent() push(`}`) // 收缩缩进 + 换行 ... return { ast, code: context.code } }在
genNode中处理其他节点类型:jsfunction genNode(node, context) { switch (node.type) { ... // 复合表达式处理 case NodeTypes.SIMPLE_EXPRESSION: genExpression(node, context) break // 表达式处理 case NodeTypes.INTERPOLATION: genInterpolation(node, context) break // {{}} 处理 case NodeTypes.COMPOUND_EXPRESSION: genCompoundExpression(node, context) break } }增加
genExpression方法,处理复合表达式js/** * 复合表达式处理 */ function genCompoundExpression(node, context) { for (let i = 0; i < node.children!.length; i++) { const child = node.children![i] if (isString(child)) { context.push(child) } else { genNode(child, context) } } }增加
genExpression方法,处理 表达式jsfunction genExpression(node, context) { const { content, isStatic } = node context.push(isStatic ? JSON.stringify(content) : content, node) }增加
genInterpolation方法,处理js/** * {{}} 处理 */ function genInterpolation(node, context) { const { push, helper } = context push(`${helper(TO_DISPLAY_STRING)}(`) genNode(node.content, context) push(`)`) }
此时运行测试实例,可以得到如下 render 函数:
const _Vue = Vue
return function render(_ctx, _cache) {
with (_ctx) {
const { toDisplayString: _toDisplayString, createElementVNode: _createElementVNode } = _Vue
return _createElementVNode("div", [], [" hello " + _toDisplayString(msg) + " "])
}
}07:响应性数据的编辑器处理:render 函数的执行处理
现在我们已经成功得到了 render 函数,但是如果我们此时运行测试实例,将得到对应的错误:
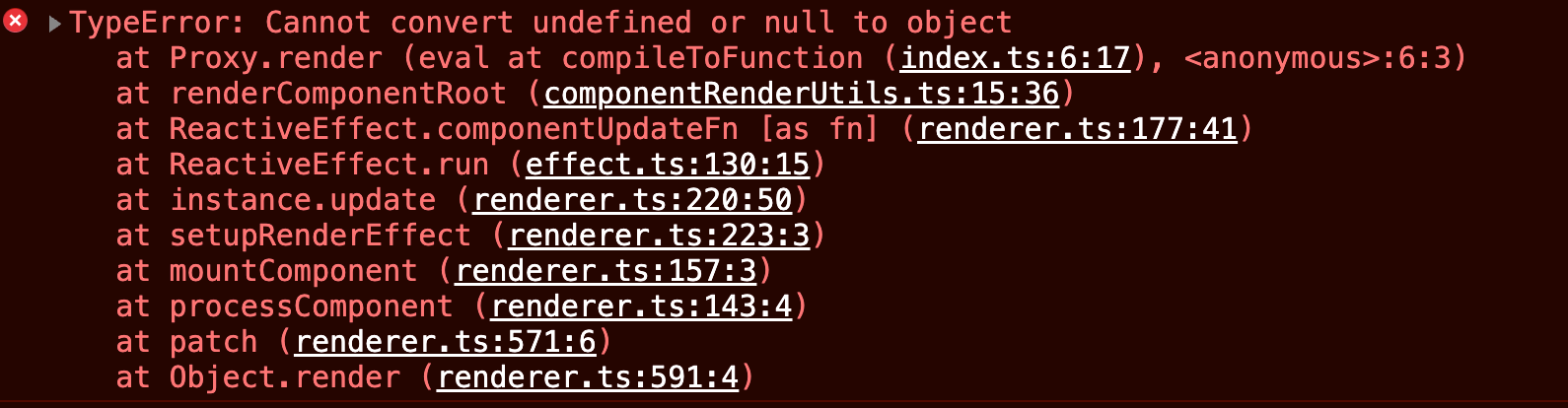
该错误指向 componentRenderUtils.ts 模块中的 renderComponentRoot :
/**
* 解析 render 函数的返回值
*/
export function renderComponentRoot(instance) { ... }那么出现该错误的原因是什么呢?
我们知道,当前的 render 函数代码为;
const _Vue = Vue
return function render(_ctx, _cache) {
with (_ctx) {
const { toDisplayString: _toDisplayString, createElementVNode: _createElementVNode } = _Vue
return _createElementVNode("div", [], [" hello " + _toDisplayString(msg) + " "])
}
}因为我们使用了 with 所以改变了 作用域 指向,即:msg 等同于 _ctx.msg。如果此时 _ctx 为 null,则会抛出对应的错误。
通过下面的实例,我们可以看的更加清楚 packages/vue/examples/compiler/with.html:
<script>
function render(_ctx) {
with (_ctx) {
console.log(msg);
}
}
const data = {
msg: 'world'
}
render.call(data, data) // 打印 "world"
render.call(data) // 报错
</script>那么由此我们就明白了,当触发 call 方法时,我们需要传递第二个参数为 data,以此作为 _ctx 的值。
所有,我们需要修改如下代码:
在
packages/runtime-core/src/componentRenderUtils.ts中:js/** * 解析 render 函数的返回值 */ export function renderComponentRoot(instance) { + // 因为存在 with,所以我们必须保证 data 不能为 undefined + const { vnode, render, data = {} } = instance let result try { // 解析到状态组件 if (vnode.shapeFlag & ShapeFlags.STATEFUL_COMPONENT) { // 获取到 result 返回值,如果 render 中使用了 this,则需要修改 this 指向 + result = normalizeVNode(render!.call(data, data)) } } catch (err) { console.error(err) } return result }创建
packages/shared/src/toDisplayString.ts,增加toDisplayString方法:js/** * 用于将 {{ Interpolation }} 值转换为显示的字符串。 * @private */ export const toDisplayString = (val: unknown): string => { return String(val) }在
packages/shared/src/index.ts中导入toDisplayString.ts模块中的所有方法:jsexport * from './toDisplayString'在
packages/vue/src/index.ts中,导入toDisplayString方法:jsexport { toDisplayString } from '@vue/shared'
此时运行测试实例,<div> hello world </div> 被正常渲染。
此时我们也可以增加对应的生命周期钩子,修改数据:
<script>
const { compile, h, render } = Vue
// 创建 template
const template = `<div> hello {{ msg }} </div>`
// 生成 render 函数
const renderFn = compile(template)
// 创建组件
const component = {
data() {
return {
msg: 'world'
}
},
render: renderFn,
created() {
setTimeout(() => {
this.msg = '世界'
}, 2000);
}
}
// 通过 h 函数,生成 vnode
const vnode = h(component)
// 通过 render 函数渲染组件
render(vnode, document.querySelector('#app'))
</script>响应式数据渲染完成。
08:多层级模板的编辑器处理:多层级的处理逻辑
在我们处理好响应式的数据处理之后,接下来我们来看一下多层级的视图渲染。
什么叫做多层级的视图渲染呢?我们来看下面的测试实例:
<script>
const { compile, h, render } = Vue
// 创建 template
const template = `<div> <h1>hello world</h1> </div>`
// 生成 render 函数
const renderFn = compile(template)
// 创建组件
const component = {
render: renderFn
}
// 通过 h 函数,生成 vnode
const vnode = h(component)
// 通过 render 函数渲染组件
render(vnode, document.querySelector('#app'))
</script>在该测试实例中,我们的 template 包含了一个子节点 h1 元素。从现在的 vue-next-mini 中运行该测试实例,大家可以发现是无法运行的。
那么如果想解析当前的子节点我们应该怎么做呢?
我们知道 compile 的作用就是把模板解析成 render 函数,我们现在看一下,现在所解析出的 render:
function render(_ctx, _cache) {
with (_ctx) {
const { createElementVNode: _createElementVNode } = _Vue
return _createElementVNode("div", [], [" ", , " "])
}
}在以上代码中,我们可以发现,没有渲染出 h1 的原因,其实就非常简单了,就是因为第三个参数 [" ", , " "]。
如果想要渲染出 h1 ,那么就需要提供出如下的 render:
function render(_ctx, _cache) {
with (_ctx) {
const { createElementVNode: _createElementVNode } = _Vue
return _createElementVNode("div", [], [" ", _createElementVNode("h1", [], ["hello world"]), " "])
}
}那么这样的 render 应该如何实现呢?
对于我们现在的代码而言,解析 render 的代码位于 packages/compiler-core/src/codegen.ts 中,该模块中包含一个 genNode 方法。
该方法是递归解析 codegenNode 的方法逻辑。那么我们可以打印一下当前的 codegenNode 来看一下:
// console.log(JSON.stringify(ast.codegenNode))
{
"type": 13,
"tag": "\"div\"",
"props": [],
"children": [
{ "type": 2, "content": " " },
{
"type": 1,
"tag": "h1",
"tagType": 0,
"props": [],
"children": [{ "type": 2, "content": "hello world" }],
"codegenNode": {
"type": 13,
"tag": "\"h1\"",
"props": [],
"children": [{ "type": 2, "content": "hello world" }]
}
},
{ "type": 2, "content": " " }
]
}从当前的 codegenNode 中可以看出,children 下,存在一个 type = 1 的节点,这个 节点就是子节点 h1。
而我们想要处理子节点渲染,就需要处理当前的 type = 1 的节点才可以。
我们知道 type = 1 对应的是 NodeTypes.ELEMENT 节点。
所以我们可以在 genNode 方法中增加如下节点处理:
/**
* 区分节点进行处理
*/
function genNode(node, context) {
switch (node.type) {
case NodeTypes.ELEMENT:
genNode(node.codegenNode!, context)
break
...
}
}经过此代码之后,我们发现 render 函数中的 h1 被成功解析,模板被成功渲染。
09:基于编辑器的指令(v-xx)处理:指令解析的整体逻辑
在 vue 中,指令是一个非常重要的环节。vue 的指令处理主要集中在 compiler 编辑器中。那么接下来我们就来看一下 vue 中的指令处理逻辑。
vue 中提供的指令非常多,大家可以点击 这里来查看所有的内置指令 ,针对于那么多的指令,我们不可能全部进行讲解实现逻辑,所以我们在这里就以 v-if 为例,来为大家讲解指令的解析与处理方案。
我们创建如下测试实例 packages/vue/examples/imooc/compiler/compiler-directive.html:
<script>
const { compile, h, render } = Vue
// 创建 template
const template = `<div> hello world <h1 v-if="isShow">你好,世界</h1> </div>`
// 生成 render 函数
const renderFn = compile(template)
console.log(renderFn.toString());
// 创建组件
const component = {
data() {
return {
isShow: false
}
},
render: renderFn
}
// 通过 h 函数,生成 vnode
const vnode = h(component)
// 通过 render 函数渲染组件
render(vnode, document.querySelector('#app'))
</script>查看生成的 render 函数:
function render(_ctx, _cache) {
with (_ctx) {
const { openBlock: _openBlock, createElementBlock: _createElementBlock, createCommentVNode: _createCommentVNode, createTextVNode: _createTextVNode } = _Vue
return (_openBlock(), _createElementBlock("div", null, [
_hoisted_1,
isShow
? (_openBlock(), _createElementBlock("h1", _hoisted_2, "你好,世界"))
: _createCommentVNode("v-if", true)
]))
}
}根据之前的经验和上面的代码可知:
with (_ctx)将改变作用域,使isShow指向data。即data.isShowisShow ? xx : xx。这个三元表达式是渲染的关键。我们v-if本质上就是一个if判断,满足条件则渲染,不满足则不渲染。
那么明确好了对应的 render 逻辑之后,接下来我们就来看对应的 ast 和 JavaScript AST:
{
"type": 0,
"children": [
{
"type": 1,
...
"children": [
{
"type": 2,
...
},
{
"type": 1, // NodeTypes.ELEMENT
"ns": 0,
"tag": "h1",
"tagType": 0,
"props": [
{
"type": 7, // NodeTypes.DIRECTIVE
"name": "if", // 指令名
// express: 表达式
"exp": {
"type": 4, // NodeTypes.SIMPLE_EXPRESSION
"content": "isShow", // 值
"isStatic": false,
"constType": 0,
"loc": {...}
},
"modifiers": [],
"loc": {...}
}
],
"isSelfClosing": false,
"children": [
{
"type": 2,
"content": "你好,世界",
"loc": {...}
}
],
"loc": {... }
}
],
...
}
],
...
}以上的 AST,我们进行了对应的简化,主要看备注部分。
由以上 AST 可知,针对于指令的处理,主要集中在 props 选项中,所以针对于 AST 而言,我们 只需要额外增加 属性(props) 的处理即可。
接下来我们来看 JavaScript AST 。
JavaScript AST 决定了最终的 render 渲染,它的处理更加复杂。我们之前创建过 transformElement 与 transformText 用来处理 element 和 text 的渲染,那么同样的道理,针对于指令的处理,我们也需要创建对应的 transformXXX 才可以进行处理。
如果以 v-if 为例,那么我们需要增加对应的 vif.ts 模块。
vif.ts 模块,需要为模块增加额外的 branches 属性,以此来处理对应的 分支指令渲染逻辑。
// 部分的 JavaScript AST
{
"type": 9,
// 分支处理
"branches": [
{
"type": 10, // NodeTypes.IF_BRANCH
"condition": {
"type": 4, // NodeTypes.SIMPLE_EXPRESSION
"content": "isShow",
"isStatic": false,
"loc": {}
},
"children": [
{
"type": 1,
"tag": "h1",
"tagType": 0,
"props": [],
"children": [{ "type": 2, "content": "你好,世界" }],
"codegenNode": {
"type": 13, // NodeTypes.VNODE_CALL
"tag": "\"h1\"",
"children": [{ "type": 2, "content": "你好,世界" }]
}
}
]
}
],
"codegenNode": {
"type": 19, // NodeTypes.JS_CONDITIONAL_EXPRESSION
"test": {
"type": 4,
"content": "isShow",
"isStatic": false,
"loc": {}
},
"consequent": {
"type": 13, // NodeTypes.VNODE_CALL
"tag": "\"h1\"",
"children": [{ "type": 2, "content": "你好,世界" }]
},
"alternate": {
"type": 14, // NodeTypes.JS_CALL_EXPRESSION
"callee": CREATE_COMMENT,
"loc": {},
"arguments": ["\"v-if\"", "true"]
},
"newline": true,
"loc": {}
}
}
...总结
到这里我们知道了,想要处理指令的编辑逻辑,那么 AST 和 JavaScript AST,我们都需要进行额外处理:
AST:额外增加props属性JavaScript AST:额外增加branches属性
10:基于编辑器的指令(v-xx)处理:AST 解析逻辑(困难)
那么首先我们先处理 AST 的解析逻辑。
我们知道 AST 的解析,主要集中在 packages/compiler-core/src/parse.ts 中。在 该模块下,存在 parseTag 方法,该方法主要用来 解析标签。那么对于我们的属性解析,也需要在该方法下进行。
该方法目前的标签解析,主要分成三部分:
- 标签开始
- 标签名
- 标签结束
根据标签 <div v-if="xx"> 的结构,我们的指令处理,应该在 标签名 - 标签结束 中间进行处理:
在
parseTag增加属性处理逻辑:js/** * 解析标签 */ function parseTag(context: any, type: TagType): any { ... // 属性与指令处理 advanceSpaces(context) let props = parseAttributes(context, type) // -- 处理标签结束部分 -- ... return { type: NodeTypes.ELEMENT, tag, tagType, // 属性与指令 props } }增加
advanceSpaces方法,处理div v-if中间的空格:js/** * 前进非固定步数 */ function advanceSpaces(context: ParserContext): void { const match = /^[\t\r\n\f ]+/.exec(context.source) if (match) { advanceBy(context, match[0].length) } }创建
parseAttributes方法,进行属性(包含attr+props)解析:js/** * 解析属性与指令 */ function parseAttributes(context, type) { // 解析之后的 props 数组 const props: any = [] // 属性名数组 const attributeNames = new Set<string>() // 循环解析,直到解析到标签结束('>' || '/>')为止 while ( context.source.length > 0 && !startsWith(context.source, '>') && !startsWith(context.source, '/>') ) { // 具体某一条属性的处理 const attr = parseAttribute(context, attributeNames) // 添加属性 if (type === TagType.Start) { props.push(attr) } advanceSpaces(context) } return props }创建
parseAttribute,处理具体的属性:js/** * 处理指定指令,返回指令节点 */ function parseAttribute(context: ParserContext, nameSet: Set<string>) { // 获取属性名称。例如:v-if const match = /^[^\t\r\n\f />][^\t\r\n\f />=]*/.exec(context.source)! const name = match[0] // 添加当前的处理属性 nameSet.add(name) advanceBy(context, name.length) // 获取属性值。 let value: any = undefined // 解析模板,并拿到对应的属性值节点 if (/^[\t\r\n\f ]*=/.test(context.source)) { advanceSpaces(context) advanceBy(context, 1) advanceSpaces(context) value = parseAttributeValue(context) } // 针对 v- 的指令处理 if (/^(v-[A-Za-z0-9-]|:|\.|@|#)/.test(name)) { // 获取指令名称 const match = /(?:^v-([a-z0-9-]+))?(?:(?::|^\.|^@|^#)(\[[^\]]+\]|[^\.]+))?(.+)?$/i.exec( name )! // 指令名。v-if 则获取 if let dirName = match[1] // TODO:指令参数 v-bind:arg // let arg: any // TODO:指令修饰符 v-on:click.modifiers // const modifiers = match[3] ? match[3].slice(1).split('.') : [] return { type: NodeTypes.DIRECTIVE, name: dirName, exp: value && { type: NodeTypes.SIMPLE_EXPRESSION, content: value.content, isStatic: false, loc: value.loc }, arg: undefined, modifiers: undefined, loc: {} } } return { type: NodeTypes.ATTRIBUTE, name, value: value && { type: NodeTypes.TEXT, content: value.content, loc: value.loc }, loc: {} } }创建
parseAttributeValue方法处理指令值:js/** * 获取属性(attr)的 value */ function parseAttributeValue(context: ParserContext) { let content = '' // 判断是单引号还是双引号 const quote = context.source[0] const isQuoted = quote === `"` || quote === `'` // 引号处理 if (isQuoted) { advanceBy(context, 1) // 获取结束的 index const endIndex = context.source.indexOf(quote) // 获取指令的值。例如:v-if="isShow",则值为 isShow if (endIndex === -1) { content = parseTextData(context, context.source.length) } else { content = parseTextData(context, endIndex) advanceBy(context, 1) } } return { content, isQuoted, loc: {} } }
至此 AST 的处理完成。解析出来的 AST 为:
{"type":0,"children":[{"type":1,"tag":"div","tagType":0,"props":[],"children":[{"type":2,"content":" hello world "},{"type":1,"tag":"h1","tagType":0,"props":[{"type":7,"name":"if","exp":{"type":4,"content":"isShow","isStatic":false,"loc":{}},"loc":{}}],"children":[{"type":2,"content":"你好,世界"}]},{"type":2,"content":" "}]}],"loc":{}}把当前 AST 替换到 vue 源码中,发现指令可以被正常渲染。
11:基于编辑器的指令(v-xx)处理:JavaScript AST ,构建 vif 转化模块(困难)
vue 内部具备非常多的指令,所以我们需要有一个统一的方法来对这些指令进行处理,在 packages/compiler-core/src/transform.ts 模块下,创建 createStructuralDirectiveTransform 方法,该方法返回一个闭包函数:
/**
* 针对于指令的处理
* @param name 正则。匹配具体的指令
* @param fn 指令的具体处理方法,通常为闭包函数
* @returns 返回一个闭包函数
*/
export function createStructuralDirectiveTransform(name: string | RegExp, fn) {
const matches = isString(name)
? (n: string) => n === name
: (n: string) => name.test(n)
return (node, context) => {
if (node.type === NodeTypes.ELEMENT) {
const { props } = node
// 结构的转换与 v-slot 无关
if (node.tagType === ElementTypes.TEMPLATE && props.some(isVSlot)) {
return
}
// 存储转化函数的数组
const exitFns: any = []
// 遍历所有的 props
for (let i = 0; i < props.length; i++) {
const prop = props[i]
// 仅处理指令,并且该指令要匹配指定的正则
if (prop.type === NodeTypes.DIRECTIVE && matches(prop.name)) {
// 删除结构指令以避免无限递归
props.splice(i, 1)
i--
// fn 会返回具体的指令函数
const onExit = fn(node, prop, context)
// 存储到数组中
if (onExit) exitFns.push(onExit)
}
}
// 返回包含所有函数的数组
return exitFns
}
}
}这里使用到了一个 isVSlot 函数,我们需要在 packages/compiler-core/src/utils.ts 中创建该函数:
/**
* 是否为 v-slot
*/
export function isVSlot(p) {
return p.type === NodeTypes.DIRECTIVE && p.name === 'slot'
}有了该函数之后,我们就可以创建 vif 模块:
创建
packages/compiler-core/src/transforms/vIf.ts模块:js/** * transformIf === exitFns。内部保存了所有 v-if、v-else、else-if 的处理函数 */ export const transformIf = createStructuralDirectiveTransform( /^(if|else|else-if)$/, (node, dir, context) => { return processIf(node, dir, context, (ifNode, branch, isRoot) => { // TODO: 目前无需处理兄弟节点情况 let key = 0 // 退出回调。当所有子节点都已完成时,完成codegenNode return () => { if (isRoot) { ifNode.codegenNode = createCodegenNodeForBranch(branch, key, context) } else { // TODO: 非根 } } }) } )构建
processIf函数,为具体的if处理函数:js/** * v-if 的转化处理 */ export function processIf( node, dir, context: TransformContext, processCodegen?: (node, branch, isRoot: boolean) => (() => void) | undefined ) { // 仅处理 v-if if (dir.name === 'if') { // 创建 branch 属性 const branch = createIfBranch(node, dir) // 生成 if 指令节点,包含 branches const ifNode = { type: NodeTypes.IF, loc: node.loc, branches: [branch] } // 切换 currentVNode,即:当前处理节点为 ifNode context.replaceNode(ifNode) // 生成对应的 codegen 属性 if (processCodegen) { return processCodegen(ifNode, branch, true) } } }创建
createIfBranch函数:js/** * 创建 if 指令的 branch 属性节点 */ function createIfBranch(node, dir) { return { type: NodeTypes.IF_BRANCH, loc: node.loc, condition: dir.exp, children: [node] } }在
packages/compiler-core/src/transform.ts中为context,添加replaceNode函数:js/** * transform 上下文对象 */ export interface TransformContext { ... /** * 替换节点 */ replaceNode(node): void } /** * 创建 transform 上下文 */ export function createTransformContext( root, { nodeTransforms = [] } ): TransformContext { const context: TransformContext = { ... replaceNode(node) { context.parent!.children[context.childIndex] = context.currentNode = node } } return context }创建
createCodegenNodeForBranch函数,为整个分支节点,添加codegen属性:js/** * 生成分支节点的 codegenNode */ function createCodegenNodeForBranch( branch, keyIndex: number, context: TransformContext ) { if (branch.condition) { return createConditionalExpression( branch.condition, createChildrenCodegenNode(branch, keyIndex), // 以注释的形式展示 v-if. createCallExpression(context.helper(CREATE_COMMENT), ['"v-if"', 'true']) ) } else { return createChildrenCodegenNode(branch, keyIndex) } }在
packages/compiler-core/src/runtimeHelpers.ts中,增加CREATE_COMMENT:jsexport const CREATE_COMMENT = Symbol(`createCommentVNode`) export const helperNameMap = { ... [CREATE_COMMENT]: 'createCommentVNode' }在
packages/compiler-core/src/ast.ts中创建createCallExpression方法:js/** * 创建调用表达式的节点 */ export function createCallExpression(callee, args) { return { type: NodeTypes.JS_CALL_EXPRESSION, loc: {}, callee, arguments: args } }在
packages/compiler-core/src/ast.ts中创建createConditionalExpression方法:js/** * 创建条件表达式的节点 */ export function createConditionalExpression( test, consequent, alternate, newline = true ) { return { type: NodeTypes.JS_CONDITIONAL_EXPRESSION, test, consequent, alternate, newline, loc: {} } }最后创建创建
createChildrenCodegenNode方法,用来处理子节点的codegen:js/** * 创建指定子节点的 codegen 节点 */ function createChildrenCodegenNode(branch, keyIndex: number) { const keyProperty = createObjectProperty( `key`, createSimpleExpression(`${keyIndex}`, false) ) const { children } = branch const firstChild = children[0] const ret = firstChild.codegenNode const vnodeCall = getMemoedVNodeCall(ret) // 填充 props injectProp(vnodeCall, keyProperty) return ret }在
packages/compiler-core/src/ast.ts中创建createObjectProperty和createSimpleExpression方法:js/** * 创建简单的表达式节点 */ export function createSimpleExpression(content, isStatic) { return { type: NodeTypes.SIMPLE_EXPRESSION, loc: {}, content, isStatic } } /** * 创建对象属性节点 */ export function createObjectProperty(key, value) { return { type: NodeTypes.JS_PROPERTY, loc: {}, key: isString(key) ? createSimpleExpression(key, true) : key, value } }在
packages/compiler-core/src/utils.ts中创建getMemoedVNodeCall方法:js/** * 返回 vnode 节点 */ export function getMemoedVNodeCall(node) { return node }最后在
packages/compiler-core/src/utils.ts中创建injectProp方法:js/** * 填充 props */ export function injectProp(node, prop) { let propsWithInjection let props = node.type === NodeTypes.VNODE_CALL ? node.props : node.arguments[2] if (props == null || isString(props)) { propsWithInjection = createObjectExpression([prop]) } if (node.type === NodeTypes.VNODE_CALL) { node.props = propsWithInjection } }该方法依赖
createObjectExpression,所以直接创建createObjectExpression方法:js/** * 创建对象表达式节点 */ export function createObjectExpression(properties) { return { type: NodeTypes.JS_OBJECT_EXPRESSION, loc: {}, properties } }
至此,我们完成了对应的 VIF 模块,接下来我们就只需要在 transform 的适当实际,触发该模块即可。
12:基于编辑器的指令(v-xx)处理:JavaScript AST ,transform 的转化逻辑
当 vif 模块构建完成之后,接下来我们就只需要在 transform 中针对 IF 使用 vif 模块进行转化即可
我们知道转化的主要方法为 traverseNode 函数,所以我们需要在该函数内增加如下代码:
export function traverseNode(node, context: TransformContext) {
...
// 循环获取节点的 transform 方法,缓存到 exitFns 中
for (let i = 0; i < nodeTransforms.length; i++) {
const onExit = nodeTransforms[i](node, context)
if (onExit) {
+ // 指令的 transforms 返回为 数组,所以需要解构
+ if (isArray(onExit)) {
+ exitFns.push(...onExit)
+ } else {
+ exitFns.push(onExit)
+ }
}
+ // 因为触发了 replaceNode,可能会导致 context.currentNode 发生变化,所以需要在这里校正
+ if (!context.currentNode) {
+ // 节点已删除
+ return
+ } else {
+ // 节点更换
+ node = context.currentNode
+ }
}
// 继续转化子节点
switch (node.type) {
+ case NodeTypes.IF_BRANCH:
case NodeTypes.ELEMENT:
case NodeTypes.ROOT:
traverseChildren(node, context)
break
// 处理插值表达式 {{}}
case NodeTypes.INTERPOLATION:
context.helper(TO_DISPLAY_STRING)
break
+ // v-if 指令处理
+ case NodeTypes.IF:
+ for (let i = 0; i < node.branches.length; i++) {
+ traverseNode(node.branches[i], context)
+ }
+ break
}
...
}至此,我们在 transform 中就拥有了处理 if 的能力。
最后我们需要在 packages/compiler-core/src/compile.ts 的 baseCompile 中增加 transformIf:
export function baseCompile(template: string, options = {}) {
const ast = baseParse(template)
transform(
ast,
extend(options, {
+ nodeTransforms: [transformElement, transformText, transformIf]
})
)
console.log(JSON.stringify(ast))
return generate(ast)
}运行测试实例 packages/vue/examples/compiler/compiler-directive.html,打印出 JavaScript AST (注意: 因为 Symbol 不会在 json 字符串下打印,所以我们需要手动加上):
{"type":0,"children":[{"type":1,"tag":"div","tagType":0,"props":[],"children":[{"type":2,"content":" hello world "},{"type":9,"branches":[{"type":10,"condition":{"type":4,"content":"isShow","isStatic":false,"loc":{}},"children":[{"type":1,"tag":"h1","tagType":0,"props":[],"children":[{"type":2,"content":"你好,世界"}],"codegenNode":{"type":13,"tag":"\"h1\"","children":[{"type":2,"content":"你好,世界"}]}}]}],"codegenNode":{"type":19,"test":{"type":4,"content":"isShow","isStatic":false,"loc":{}},"consequent":{"type":13,"tag":"\"h1\"","children":[{"type":2,"content":"你好,世界"}]},"alternate":{"type":14,"callee": CREATE_COMMENT,"loc":{},"arguments":["\"v-if\"","true"]},"newline":true,"loc":{}}},{"type":2,"content":" "}],"codegenNode":{"type":13,"tag":"\"div\"","props":[],"children":[{"type":2,"content":" hello world "},{"type":9,"branches":[{"type":10,"condition":{"type":4,"content":"isShow","isStatic":false,"loc":{}},"children":[{"type":1,"tag":"h1","tagType":0,"props":[],"children":[{"type":2,"content":"你好,世界"}],"codegenNode":{"type":13,"tag":"\"h1\"","children":[{"type":2,"content":"你好,世界"}]}}]}],"codegenNode":{"type":19,"test":{"type":4,"content":"isShow","isStatic":false,"loc":{}},"consequent":{"type":13,"tag":"\"h1\"","children":[{"type":2,"content":"你好,世界"}]},"alternate":{"type":14,"callee": CREATE_COMMENT,"loc":{},"arguments":["\"v-if\"","true"]},"newline":true,"loc":{}}},{"type":2,"content":" "}]}}],"loc":{},"codegenNode":{"type":13,"tag":"\"div\"","props":[],"children":[{"type":2,"content":" hello world "},{"type":9,"branches":[{"type":10,"condition":{"type":4,"content":"isShow","isStatic":false,"loc":{}},"children":[{"type":1,"tag":"h1","tagType":0,"props":[],"children":[{"type":2,"content":"你好,世界"}],"codegenNode":{"type":13,"tag":"\"h1\"","children":[{"type":2,"content":"你好,世界"}]}}]}],"codegenNode":{"type":19,"test":{"type":4,"content":"isShow","isStatic":false,"loc":{}},"consequent":{"type":13,"tag":"\"h1\"","children":[{"type":2,"content":"你好,世界"}]},"alternate":{"type":14,"callee": CREATE_COMMENT,"loc":{},"arguments":["\"v-if\"","true"]},"newline":true,"loc":{}}},{"type":2,"content":" "}]},"helpers":[CREATE_ELEMENT_VNODE, CREATE_COMMENT],"components":[],"directives":[],"imports":[],"hoists":[],"temps":[],"cached":[]}直接把以上内容复制到 vue3 源码的 generate 方法调用处(替换 ast),页面可正常渲染。证明当前的 JavaScript AST 处理完成。
13:基于编辑器的指令(v-xx)处理:生成 render 函数
当 JavaScript AST 构建完成之后,最后我们只需要生成对应的 render 函数即可。
const _Vue = Vue
return function render(_ctx, _cache) {
with (_ctx) {
const { createElementVNode: _createElementVNode, createCommentVNode: _createCommentVNode } = _Vue
return _createElementVNode("div", [], [
" hello world ",
isShow
? _createElementVNode("h1", null, ["你好,世界"])
: _createCommentVNode("v-if", true),
" "
])
}
}依据以上模板,可以看出,render 的核心处理在于 当前的 三元表达式(children)处理:
[
" hello world ",
isShow
? _createElementVNode("h1", null, ["你好,世界"])
: _createCommentVNode("v-if", true),
" "
]而对于 codegen 模块而言,解析当前参数的函数为 genNode,所以我们需要在 genNode 中增加对应的节点处理:
在
packages/compiler-core/src/codegen.ts中的genNode方法下,增加节点处理:jsfunction genNode(node, context) { switch (node.type) { case NodeTypes.ELEMENT: case NodeTypes.IF: genNode(node.codegenNode!, context) break ... // JS调用表达式的处理 case NodeTypes.JS_CALL_EXPRESSION: genCallExpression(node, context) break // JS条件表达式的处理 case NodeTypes.JS_CONDITIONAL_EXPRESSION: genConditionalExpression(node, context) break } }创建
genCallExpression方法:js/** * JS调用表达式的处理 */ function genCallExpression(node, context) { const { push, helper } = context const callee = isString(node.callee) ? node.callee : helper(node.callee) push(callee + `(`, node) genNodeList(node.arguments, context) push(`)`) }创建
genConditionalExpression方法:js/** * JS条件表达式的处理。 * 例如: * isShow ? _createElementVNode("h1", null, ["你好,世界"]) : _createCommentVNode("v-if", true), */ function genConditionalExpression(node, context) { const { test, consequent, alternate, newline: needNewline } = node const { push, indent, deindent, newline } = context if (test.type === NodeTypes.SIMPLE_EXPRESSION) { // 写入变量 genExpression(test, context) } // 换行 needNewline && indent() // 缩进++ context.indentLevel++ // 写入空格 needNewline || push(` `) // 写入 ? push(`? `) // 写入满足条件的处理逻辑 genNode(consequent, context) // 缩进 -- context.indentLevel-- // 换行 needNewline && newline() // 写入空格 needNewline || push(` `) // 写入: push(`: `) // 判断 else 的类型是否也为 JS_CONDITIONAL_EXPRESSION const isNested = alternate.type === NodeTypes.JS_CONDITIONAL_EXPRESSION // 不是则缩进++ if (!isNested) { context.indentLevel++ } // 写入 else (不满足条件)的处理逻辑 genNode(alternate, context) // 缩进-- if (!isNested) { context.indentLevel-- } // 控制缩进 + 换行 needNewline && deindent() }
至此,generate 处理完成。
此时生成的 render 函数为:
const _Vue = Vue
return function render(_ctx, _cache) {
with (_ctx) {
const { createElementVNode: _createElementVNode, createCommentVNode: _createCommentVNode } = _Vue
return _createElementVNode("div", [], [" hello world ", isShow
? _createElementVNode("h1", null, ["你好,世界"])
: _createCommentVNode("v-if", true)
, " "])
}
}在上述 render 中,因为使用了 createCommentVNode ,所以我们需要创建并导出该函数。
在
packages/runtime-core/src/vnode.ts中,创建该函数:js/** * 创建注释节点 */ export function createCommentVNode(text) { return createVNode(Comment, null, text) }在
packages/runtime-core/src/index.ts中导出:jsexport { ... createCommentVNode } from './vnode'在
packages/vue/src/index.ts中导出:jsexport { ... createCommentVNode } from '@vue/runtime-core'
运行测试实例,效果可以正常展示。
同时,我们可以修改 isShow 的值,增加一个延迟的数据变化:
<script>
const { compile, h, render } = Vue
// 创建 template
const template = `<div> hello world <h1 v-if="isShow">你好,世界</h1> </div>`
// 生成 render 函数
const renderFn = compile(template)
console.log(renderFn.toString());
// 创建组件
const component = {
data() {
return {
isShow: false
}
},
render: renderFn,
created() {
setTimeout(() => {
this.isShow = true
}, 2000);
}
}
// 通过 h 函数,生成 vnode
const vnode = h(component)
// 通过 render 函数渲染组件
render(vnode, document.querySelector('#app'))
</script>响应式的数据渲染,依然可以正常展示。
14:总结
那么到这里,咱们的编辑器处理,我们就已经全部完成了。
在本章中我们对编辑器进行了一些深入的了解,对于编辑器而言,本质上就是把 template 转化为 render 函数。
对于指令或者 而言,本质只是模板解析的一部分,所以这部分的核心处理逻辑都是在编辑器中进行的。
而对于指令而言,每一个指令的处理都会对应一个 transformXX 函数,这个函数的存在本质上是为了生成一个对应的 属性节点 ,以便在 generate 时,进行对应的解析。