一、编写高质量代码
1. Array Flatten
- 写一个JS函数,实现数组扁平化,只减少一级嵌套
- 如输入[1,[2,[3]],4],输出[1,2,[3],4]
思路:
- 定义空数组
arr = []。遍历当前数组 - 如果
item非数组,则累加到arr - 如果
item是数组,则遍历之后累加到arrjs/** * 数组扁平化 使用 push * @param arr arr */ export function arrayFlatten (arr) { const res = []; arr.forEach(item => { if (Array.isArray(item)) { item.forEach(n => res.push(n)); } else { res.push(item); } }) return res; } /** * 数组扁平化 使用 concat * @param arr arr */ export function arrayFlatten (arr) { let res = []; arr.forEach(item => { res = res.concat(item); }) return res; }
- 定义空数组
连环问:
Array Flatten彻底拍平- 写一个
JS函数,实现数组扁平化,减少所有嵌套的层级 - 如输入[1,[2,[3]],4],输出[1,2,3,4]
- 思路:先实现一级扁平化,然后递归调用,直到全部扁平js
/** * 数组扁平化 使用 push * @param arr arr */ export function arrayFlatten (arr) { const res = []; arr.forEach(item => { if (Array.isArray(item)) { // 递归 const flatItem = arrayFlatten(item); flatItem.forEach(n => res.push(n)) } else { res.push(item); } }) return res; } /** * 数组扁平化 使用 concat * @param arr arr */ export function arrayFlatten (arr) { let res = []; arr.forEach(item => { if (Array.isArray(item)) { const flatItem = arrayFlatten(item); res = res.concat(flatItem); } else { res = res.concat(item); } }) return res; } // 巧妙的解决方案:toString() const nums = [1, 2, [3, 4, [100, 200], 5], 6]; nums.toString() // '1,2,3,4,100,200,5,6' // 但 万一数组元素是 {x: 100} 等引用类型,就不可以了
- 写一个
2. 获取类型
- 手写一个 getType 函数,传入任意变量,可准确获取类型
- 如 number string boolean 等值类型
- 还有 object array map regexp 等引用类型
答案:
- 使用 Object.prototype.toString.call(x)
- 注意,不能直接调用 x.toString()js
export function getType(x) { const originType = Object.prototype.toString.call(x); const spaceIndex = originType.indexOf(' '); const type = originType.slice(spaceIndex + 1, -1); return type.toLocaleLowerCase() }
解析
常见的类型判断
typeof: 只能判断值类型,其他就是function和objectinstanceof: 需要两个参数来判断,而不是获取类型
枚举各种类型
- 通过
typeof判断值类型和function - 其他引用通过 instanceof 来逐个判断识别
- 如 x instanceof Map, 则返回 map
- 枚举的坏处
- 可能忽略某些类型
- 增加了新类型,需要修改代码js
export function getType(x) { // 通过 typeof 判断值类型和 function // 其余的 'object' 通过 instanceof 枚举 if (typeof x === 'object') { if (x instanceof Array) return 'array'; if (x instanceof Map) return 'map'; return 'object' } }
- 通过
3. new 一个对象发生了什么? 请手写代码表示
class 是 function 的语法糖
tsclass Foo { name: string; city: string; constructor(name: string) { this.name = name; this.city = '北京'; } getName() { return this.name; } } const f = new Foo('张三')jsfunction Foo(name) { this.name = name; this.city= '北京'; } Foo.prototype.getName = function () {return this.name} const f = new Foo('张三')过程
- 创建一个空对象 obj, 继承构造函数的原型
- 执行构造函数(将 obj 作为 this)
- 返回 objts
export function customNew<T>(constructor: Function, ...args: any[]): T { // 1. 创建一个空对象,继承 constructor 的原型 const obj = Object.create(constructor.prototype); // 2. 将 obj 作为 this, 执行 constructor, 传入参数 constructor.apply(obj, args); // 3. 返回 obj return obj; } const f1 = customNew<Foo>(Foo, '张三')
连环问:Object.create 和 {} 有什么区别?
- {} 创建空对象,原型指向 object.prototype。
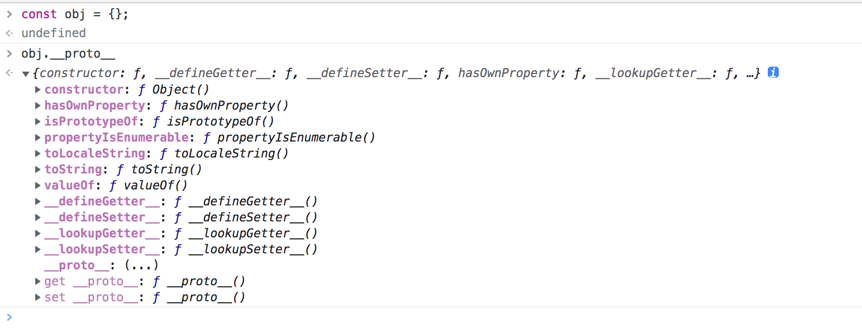
- Object.create 创建空对象,原型指向传入的参数。
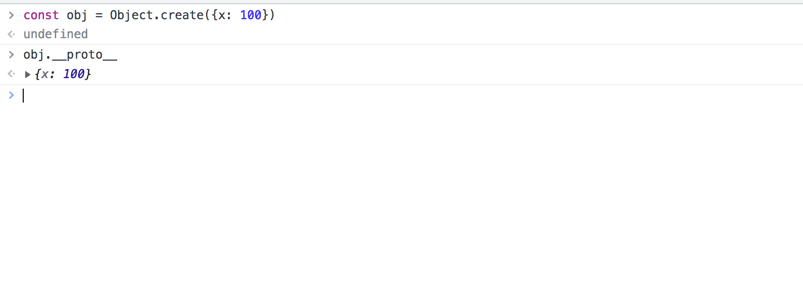
- {} 创建空对象,原型指向 object.prototype。
4. 遍历 DOM 树
给一个 DOM 树
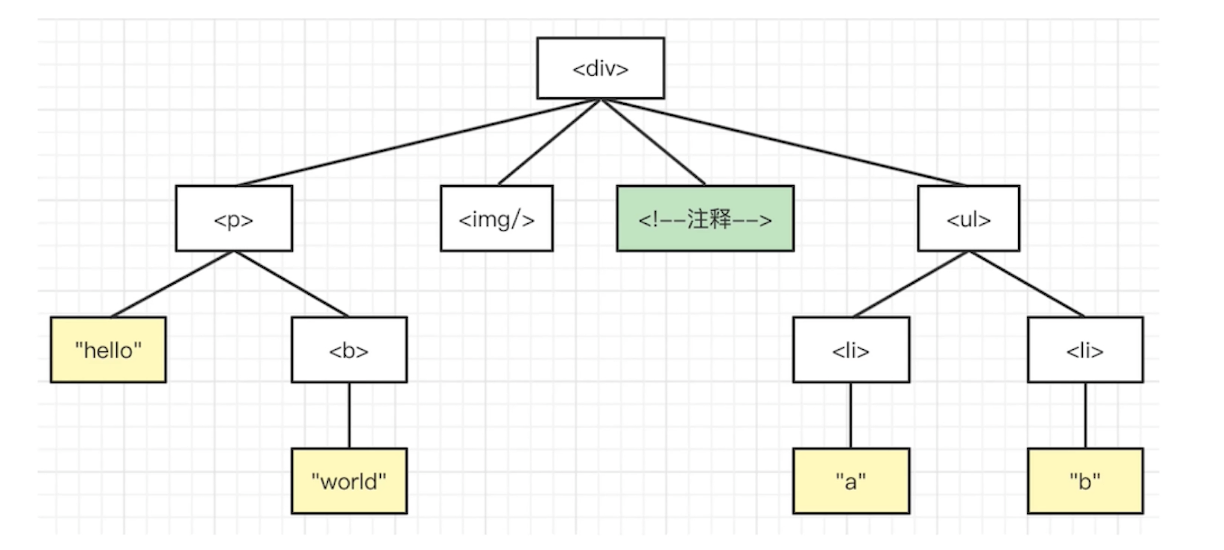
- 深度优先遍历,结果会输出什么?
- 广度优先遍历,结果会输出什么?
实现
ts/** * 访问节点 * @param n node */ function visitNode(n: Node) { if (n instanceof Comment) { // 注释 console.info('Comment node --->', n.textContent); } if (n instanceof Text) { // 文本 const t = n.textContent?.trim() if (t) { console.info('Text node --->', t) } } if (n instanceof HTMLElement) { // element console.info('Element node --->', `<${n.tagName.toLowerCase()}>`) } } /** * 深度优先遍历 递归 * @param root */ function depthFirstTraverse(root: Node) { visitNode(root); // .childNodes【包括文本和注释】 和 children 不一样 const childNodes = root.childNodes; if (childNodes.length) { childNodes.forEach(child => { // 递归 depthFirstTraverse(child) }) } } /** * 深度优先遍历 用栈 * @param root */ function depthFirstTraverseStack(root: Node) { const stack: Node[] = []; // 根节点压栈 stack.push(root) while (stack.length > 0) { const curNode = stack.pop() // 出栈 if (curNode === null) break visitNode(curNode) const childNodes = curNode.childNodes; if (childNodes.length > 0) { // reverse 反顺序压栈 Array.from(childNodes).reverse().forEach(child => stack.push(child)); } } } /** * 广度优先 * @param root */ function breadthFirstTraverse(root: Node) { // 数组 const queue: Node[] = [] // 根节点入队列 while (queue.length > 0) { const curNode = queue.pop(); if (curNode === null) break; visitNode(root) // 子节点入队 const childNodes = curNode.childNodes; if (childNodes.length) { childNodes.forEach(child => queue.unshift(child)) } } } const box = document.getElementById('box')!; // if (box === null) throw new Error('box is null'); depthFirstTraverse(box) breadthFirstTraverse(box)重点
- 深度优先,递归、贪心
- 广度优先,使用队列(数组 vs 链表)
- children 和 childNodes 不同
连环问:深度优先遍历可以不用递归吗? 答案:
- 可以不用递归,用栈
- 因为递归本身就是栈ts
/** * 深度优先遍历 用栈 * @param root */ function depthFirstTraverseStack(root: Node) { const stack: Node[] = []; // 根节点压栈 stack.push(root) while (stack.length > 0) { const curNode = stack.pop() // 出栈 if (curNode === null) break visitNode(curNode) const childNodes = curNode.childNodes; if (childNodes.length > 0) { // reverse 反顺序压栈 Array.from(childNodes).reverse().forEach(child => stack.push(child)); } } } - 递归 VS 非递归
- 递归逻辑更加清晰,但容易发生 stack overflow 错误
- 非递归效率更高,但逻辑比较复杂
5. 手写 LazyMan
- 支持 sleep 和 eat 两个方法
- 支持链式调用text
const lm = new LazyMan("张三"); lm.eat('苹果').eat('香蕉').sleep(5).eat('葡萄'); // 打印如下: // '张三 eat 苹果' // '张三 eat 香蕉' // (等待 5s) // '张三 eat 葡萄' - 代码设计
由于有 sleep 功能,函数不能直接在调用时触发
初始化一个列表,把函数注册进去
由每个 item 触发 next 执行(遇到 sleep 则异步触发)
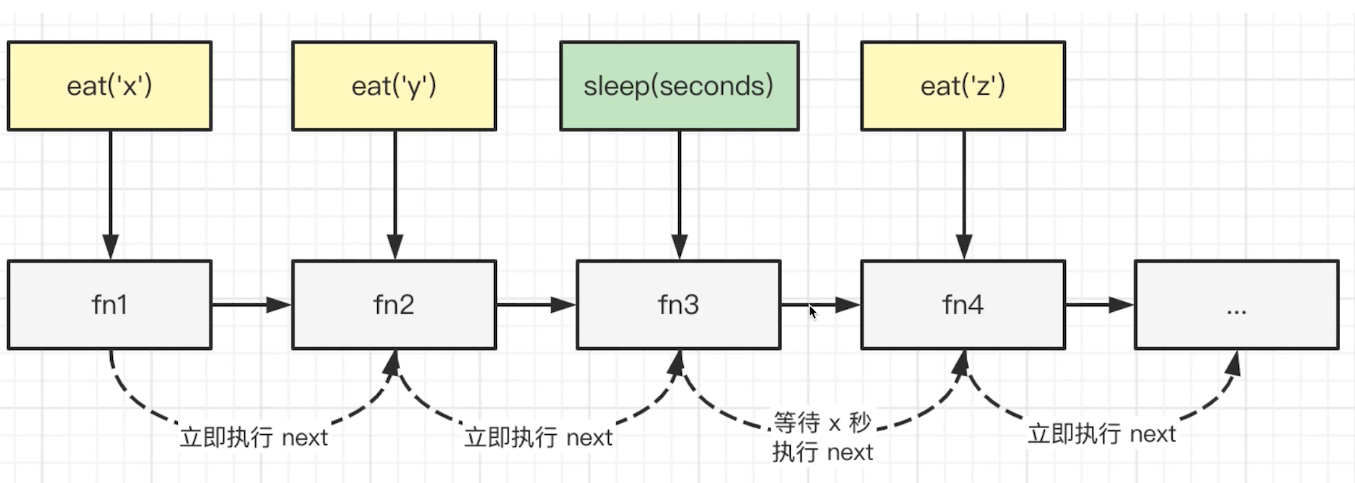 ts
tsclass LazyMan { private readonly name: string = ''; private tasks: Function[] = []; // 任务列表 constructor(name: string) { this.name = name; setTimeout(() => { this.next() }) } private next() { const task = this.tasks.shift(); // 取出当前 tasks 的第一个任务 if (task) task() } eat(food: string) { const task = () => { console.info(`${this.name} eat ${food}`); this.next() // 立刻执行下一个任务 } this.tasks.push(task); return this; } sleep(seconds: number) { const task = () => { console.info(`${this.name} 开始睡觉 ${seconds}s`) setTimeout(() => { console.info(`${this.name} 已经睡完了 ${seconds}s`) this.next(); }, seconds * 1000) } this.tasks.push(task) return this; } }重点
- 任务队列
- 触发 next
- sleep 异步触发
6. 手写一个 curry 函数,把其他函数柯里化
- 分析
- curry 返回的是一个函数 fn
- 执行 fn,中间状态返回函数,如 add(1) 或者 add(1)(2)
- 最后返回执行结果,如 add(1)(2)(3)ts
export function curry(fn: Function) { const fnArgsLen = fn.length; // 传入函数的参数长度 let args: any[] = []; function calc(this: any, ...newArgs: any[]) { // 积累参数 args = [ ...args, ...newArgs ] if (args.length < fnArgsLen) { // 参数不够,返回函数 return calc; } else { // 参数够了,返回执行结果 return fn.apply(this, args.slice(0, fnArgsLen)); } } return calc; } function add(a: number, b: number, c: number) { return a + b + c; } const curryAdd = curry(add); const res = curryAdd(10)(20)(30); console.log(res)
7. instanceof 原理是什么,请用代码表示
- instanceof 原理
例如 f instanceof Foo
顺着 f.__proto__向上查找(原型链)
看能否找到 Foo.prototype
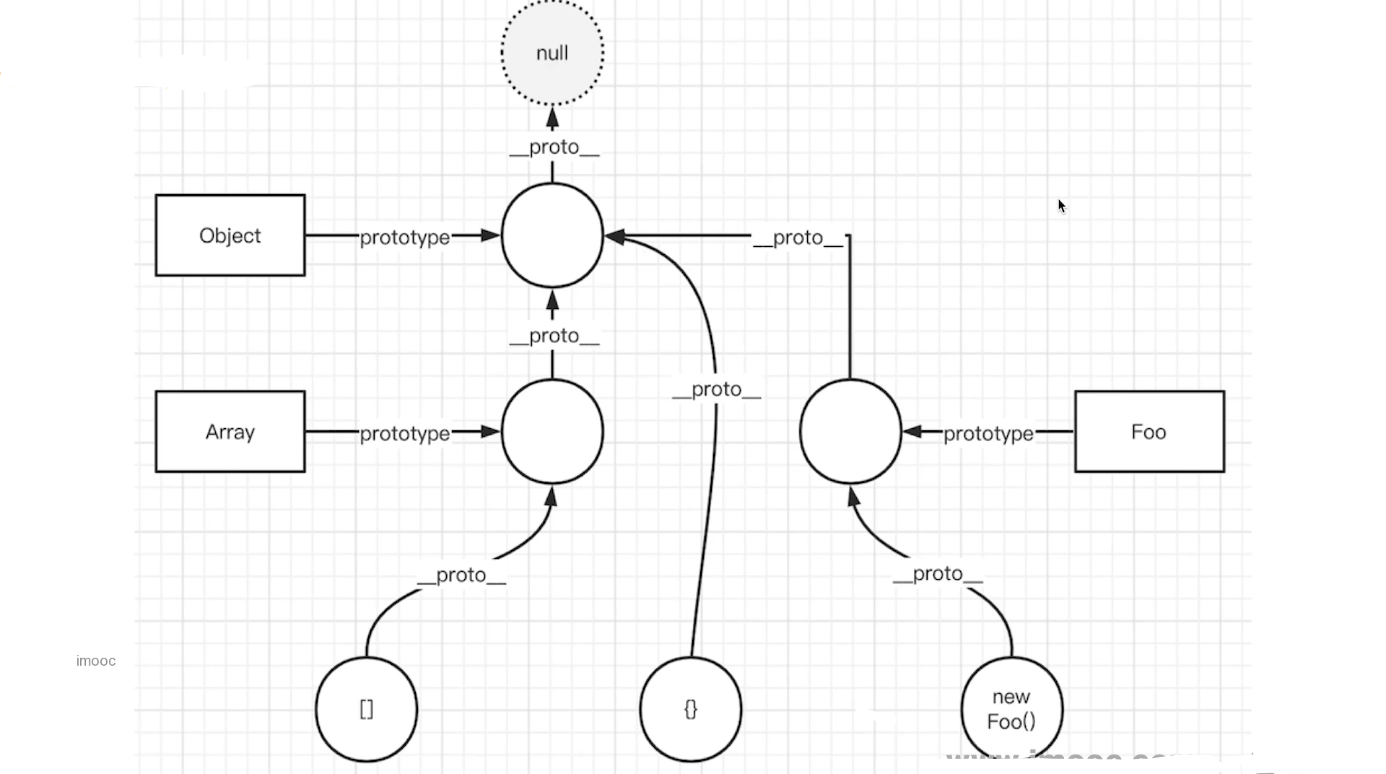 ts
tsexport function myInstanceof(instance: any, origin: any): boolean { if (instance === null) return false; // null undefined const type = typeof instance; if (type !== 'object' && type !== 'function') { // 值类型 return false } let tempInstance = instance; // 为了防止修改 instance while (tempInstance) { if (tempInstance.__proto__ === origin.__proto) { return true; } // 未匹配 tempInstance = tempInstance.__proto__ // 顺着原型链,往上找 } return false } console.info(myInstanceof({}, Object)) console.info(myInstanceof([], Object)) console.info(myInstanceof([], Array))重点
- JS 原型和原型链
- 通过 while 循环一直向上查找原型链
8. 手写函数 bind
bind 应用
- 返回一个新函数,但是不会执行
- 绑定 this 和 部分参数
- 如果是箭头函数,无法改变 this,只能改变参数
分析
- 返回新函数
- 绑定 this
- 同时绑定执行时的参数(apply 或者 call)ts
// @ts-ignore Function.prototype.customBind = function (context: any, ...bindArgs: any[]) { // context 是 bind 传入的 this // bindArgs 是 bind 传入的各个参数 const self = this; // 当前函数本身 return function (...args: any[]) { // 拼接参数 const newArgs = bindArgs.concat(args); return self.apply(context, newArgs) } } // 测试 function fn(this:any, a: any, b: any, c: any) { console.info(this, a, b, c) } // @ts-ignore const fn1 = fn.customBind({x: 100}, 10); fn1(20, 30);
连环问:手写函数 call 和 apply
- call 和 apply 应用
- bind 返回一个新函数(不执行),call 和 apply 会立即执行函数
- 绑定 this
- 传入执行参数
- 分析:如何在函数执行时绑定 this
- 如 const obj = {x: 100, fn() {this.x}}
- 执行 obj.fn(),此时 fn 内部的this 就指向 obj
- 可借此来实现函数绑定 thists
// @ts-ignore Function.prototype.customCall = function (context: any, ...args: any[]) { if (context === null) context = globalThis; if (typeof context !== 'object') context = new Object(context); // 值类型,变成引用类型 const fnKey = Symbol(); // 不会出现属性名称的覆盖 context[fnKey] = this; // this 就是当前的函数 const res = context[fnKey](...args); // 绑定了 this delete context[fnKey]; // 清理掉 fn,防止污染 return res; } // @ts-ignore Function.prototype.customApply = function (context: any, args: any[] = []) { if (context === null) context = globalThis; if (typeof context !== 'object') context = new Object(context); // 值类型,变成引用类型 const fnKey = Symbol(); // 不会出现属性名称的覆盖 context[fnKey] = this; // this 就是当前的函数 const res = context[fnKey](...args); // 绑定了 this delete context[fnKey]; // 清理掉 fn,防止污染 return res; } // 测试 function fn(this:any, a: any, b: any, c: any) { console.info(this, a, b, c) } // @ts-ignore fn.customCall({x: 100}, 10, 20, 30);
- 重点
- 想用 call 实现 apply,用 apply 实现 call。这不可取
- 原生 call apply 的 this 如果是值类型,也会被 new Object(...)
- Symbol 的作用
- call 和 apply 应用
9. 手写 EventBus 自定义事件
on once
emit
off
分析
- on 和 once 注册函数,存储起来
- emit 时找到对应的函数,执行
- off 找到对应的函数,从对象中删除
- 注意区分 on 和 once
- on 绑定的事件可以连续执行,除非 off
- once 绑定的函数 emit 一次即删除,也可以未执行而被 off
- 数据结构上标识出 on 和 once
- 方式一:ts
class EventBus { /** * { * 'key1': [ * { * fn: fn1, isOnce: false, * fn: fn2, isOnce: false, * fn: fn3, isOnce: true * } * ], * 'key2': [], * 'key3': [] * } */ private events: { [key: string]: Array<{fn: Function, isOnce: boolean}> } constructor() { this.events = {} } on(type: string, fn: Function, isOnce: boolean = false) { const events = this.events; if (events[type] === null) { events[type] = []; // 初始化 key 的 fn 数组 } events[type].push({fn, isOnce}) } once(type: string, fn: Function ) { this.on(type, fn, true) } off(type: string, fn?: Function) { if (!fn) { // 解绑所有 type 的函数 this.events[type] = [] } else { // 解绑单个 fn const fnList = this.events[type]; if (fnList) { this.events[type] = fnList.filter(item => item.fn !== fn); } } } emit(type: string, ...args: any[]) { const fnList = this.events[type] if (fnList === null) return; this.events[type] = fnList.filter(item => { const {fn, isOnce } = item; fn(...args); // once 执行一次就要被过滤掉 if (!isOnce) return true; return false }) } } const e = new EventBus(); function fn1(a: any, b: any) { console.log('fn1', a, b) } function fn2(a: any, b: any) { console.log('fn2', a, b) } function fn3(a: any, b: any) { console.log('fn3', a, b) } e.on('key1', fn1) e.on('key1', fn2) e.once('key1', fn3) e.on('xxx', fn3) e.emit('key1', 10, 20) // 触发 fn1 fn2 fn3 e.off('key1', fn1) e.emit('key1', 10, 20) // 触发 fn2 - 方式二:ts
export default class EventBus2 { private events: { [key: string]: Array<Function> } // { key1: [fn1, fn2], key2: [fn1, fn2] } private onceEvents: { [key: string]: Array<Function> } constructor() { this.events = {} this.onceEvents = {} } on(type: string, fn: Function) { const events = this.events if (events[type] == null) events[type] = [] events[type].push(fn) } once(type: string, fn: Function) { const onceEvents = this.onceEvents if (onceEvents[type] == null) onceEvents[type] = [] onceEvents[type].push(fn) } off(type: string, fn?: Function) { if (!fn) { // 解绑所有事件 this.events[type] = [] this.onceEvents[type] = [] } else { // 解绑单个事件 const fnList = this.events[type] const onceFnList = this.onceEvents[type] if (fnList) { this.events[type] = fnList.filter(curFn => curFn !== fn) } if (onceFnList) { this.onceEvents[type] = onceFnList.filter(curFn => curFn !== fn) } } } emit(type: string, ...args: any[]) { const fnList = this.events[type] const onceFnList = this.onceEvents[type] if (fnList) { fnList.forEach(f => f(...args)) } if (onceFnList) { onceFnList.forEach(f => f(...args)) // once 执行一次就删除 this.onceEvents[type] = [] } } } // const e = new EventBus2() // function fn1(a: any, b: any) { console.log('fn1', a, b) } // function fn2(a: any, b: any) { console.log('fn2', a, b) } // function fn3(a: any, b: any) { console.log('fn3', a, b) } // e.on('key1', fn1) // e.on('key1', fn2) // e.once('key1', fn3) // e.on('xxxxxx', fn3) // e.emit('key1', 10, 20) // 触发 fn1 fn2 fn3 // e.off('key1', fn1) // e.emit('key1', 100, 200) // 触发 fn2
10. 用 js 实现一个 LRU 缓存
什么是 LRU 缓存
- LRU - Least Recently Used 最近使用
- 如果内存优先,只缓存最近使用的,删除"沉水"数据
- 核心 API 两个: get set
分析
- 用哈希表存储数据,这样 get set 才够快 O(1)
- 必须是有序的,常见数据放在前面,"沉水" 数据放在后面
- 哈希表 + 有序,就是 Map —— 其他都不行
代码实现
ts/** * @description LRU cache * @author 双越老师 */ export default class LRUCache { private length: number private data: Map<any, any> = new Map() constructor(length: number) { if (length < 1) throw new Error('invalid length') this.length = length } set(key: any, value: any) { const data = this.data if (data.has(key)) { data.delete(key) } data.set(key, value) if (data.size > this.length) { // 如果超出了容量,则删除 Map 最老的元素 const delKey = data.keys().next().value data.delete(delKey) } } get(key: any): any { const data = this.data if (!data.has(key)) return null const value = data.get(key) data.delete(key) data.set(key, value) return value } } // const lruCache = new LRUCache(2) // lruCache.set(1, 1) // {1=1} // lruCache.set(2, 2) // {1=1, 2=2} // console.info(lruCache.get(1)) // 1 {2=2, 1=1} // lruCache.set(3, 3) // {1=1, 3=3} // console.info(lruCache.get(2)) // null // lruCache.set(4, 4) // {3=3, 4=4} // console.info(lruCache.get(1)) // null // console.info(lruCache.get(3)) // 3 {4=4, 3=3} // console.info(lruCache.get(4)) // 4 {3=3, 4=4}重点
- 选择合理数据结构
连环问:不用 Map 如何实现 LRU 缓存?
- LRU 使用 Map 是基本两个特点
- 哈希表(get set 速度快)
- 有序
- 可结合 Object + Array
- 存在性能问题:Array 操作慢
- 移除 "沉水"数据,用数组 shift 效率太低。
- get set 是移动数据,用数组 splice 效率太低
- 把数组改为双向链表
- 可快速增减元素
- 可快速删除元素
- 可快速移动元素位置
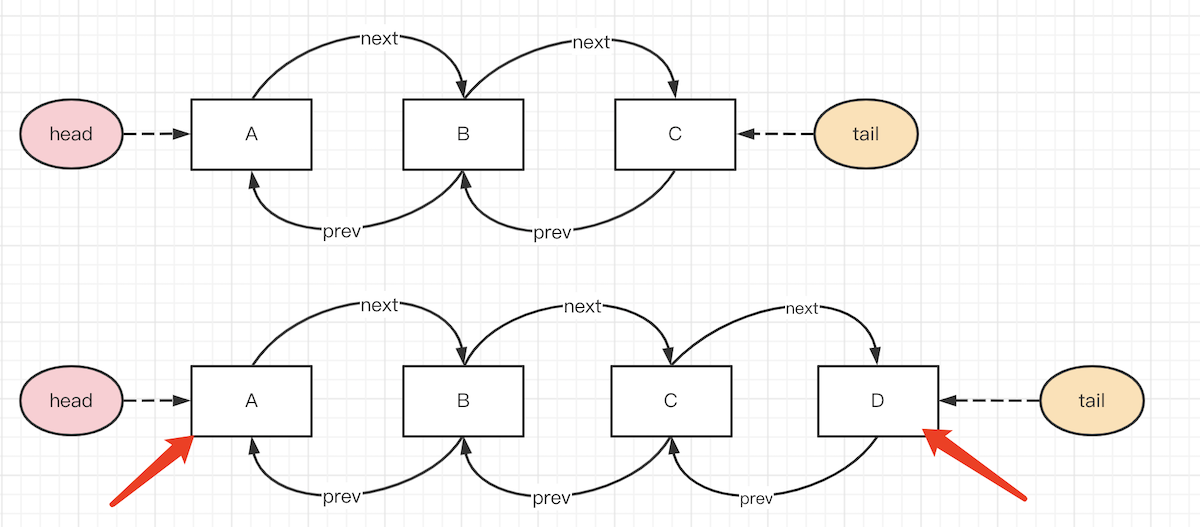
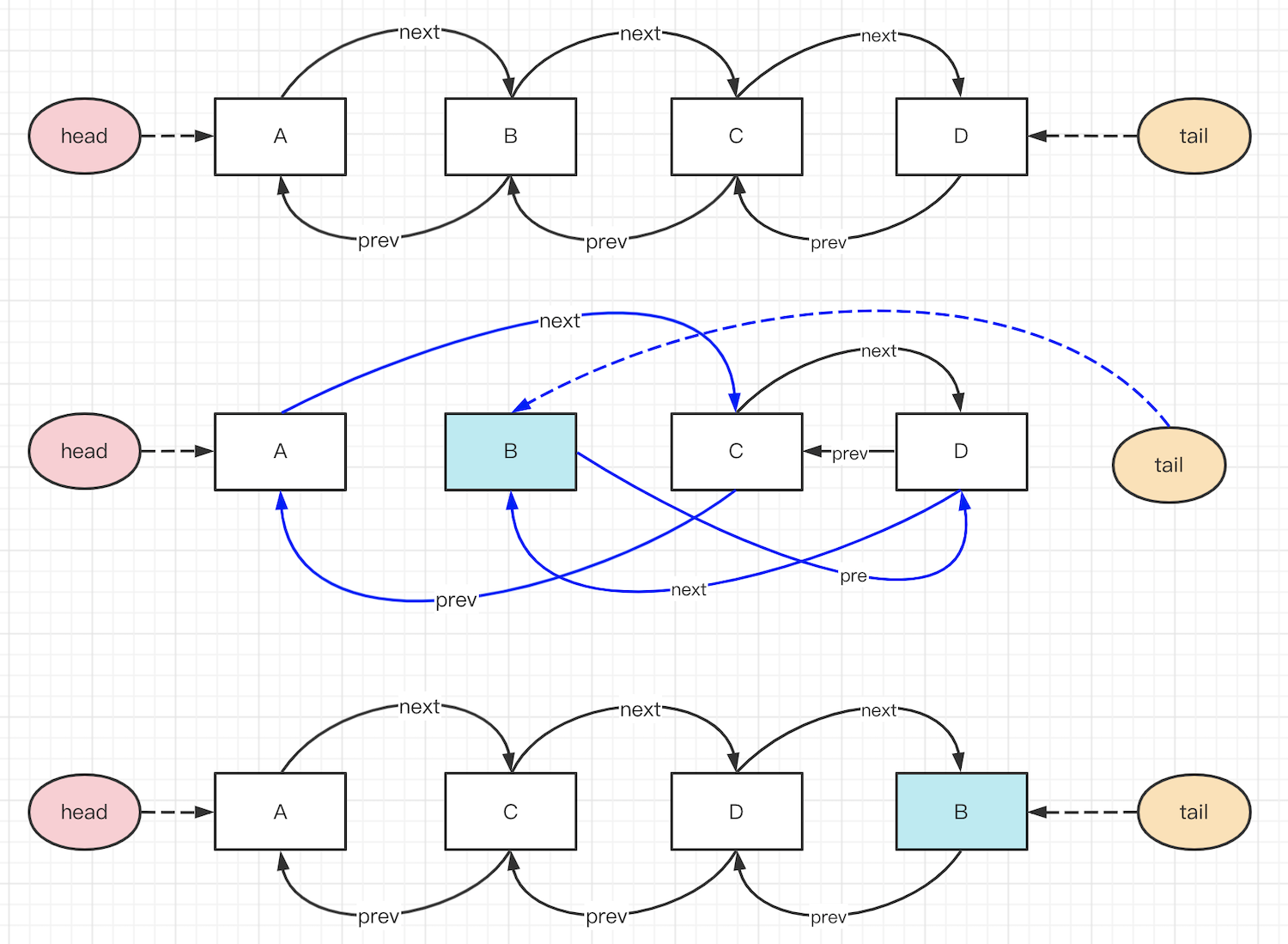
- 代码实现ts
/** * @description LRU 缓存 - 不使用 Map * @author 双越老师 */ interface IListNode { value: any key: string // 存储 key ,方便删除(否则删除时就需要遍历 this.data ) prev?: IListNode next?: IListNode } export default class LRUCache { private length: number private data: { [key: string]: IListNode } = {} private dataLength: number = 0 private listHead: IListNode | null = null private listTail: IListNode | null = null constructor(length: number) { if (length < 1) throw new Error('invalid length') this.length = length } private moveToTail(curNode: IListNode) { const tail = this.listTail if (tail === curNode) return // -------------- 1. 让 prevNode nextNode 断绝与 curNode 的关系 -------------- const prevNode = curNode.prev const nextNode = curNode.next if (prevNode) { if (nextNode) { prevNode.next = nextNode } else { delete prevNode.next } } if (nextNode) { if (prevNode) { nextNode.prev = prevNode } else { delete nextNode.prev } if (this.listHead === curNode) this.listHead = nextNode } // -------------- 2. 让 curNode 断绝与 prevNode nextNode 的关系 -------------- delete curNode.prev delete curNode.next // -------------- 3. 在 list 末尾重新建立 curNode 的新关系 -------------- if (tail) { tail.next = curNode curNode.prev = tail } this.listTail = curNode } private tryClean() { while (this.dataLength > this.length) { const head = this.listHead if (head == null) throw new Error('head is null') const headNext = head.next if (headNext == null) throw new Error('headNext is null') // 1. 断绝 head 和 next 的关系 delete headNext.prev delete head.next // 2. 重新赋值 listHead this.listHead = headNext // 3. 清理 data ,重新计数 delete this.data[head.key] this.dataLength = this.dataLength - 1 } } get(key: string): any { const data = this.data const curNode = data[key] if (curNode == null) return null if (this.listTail === curNode) { // 本身在末尾(最新鲜的位置),直接返回 value return curNode.value } // curNode 移动到末尾 this.moveToTail(curNode) return curNode.value } set(key: string, value: any) { const data = this.data const curNode = data[key] if (curNode == null) { // 新增数据 const newNode: IListNode = { key, value } // 移动到末尾 this.moveToTail(newNode) data[key] = newNode this.dataLength++ if (this.dataLength === 1) this.listHead = newNode } else { // 修改现有数据 curNode.value = value // 移动到末尾 this.moveToTail(curNode) } // 尝试清理长度 this.tryClean() } } // const lruCache = new LRUCache(2) // lruCache.set('1', 1) // {1=1} // lruCache.set('2', 2) // {1=1, 2=2} // console.info(lruCache.get('1')) // 1 {2=2, 1=1} // lruCache.set('3', 3) // {1=1, 3=3} // console.info(lruCache.get('2')) // null // lruCache.set('4', 4) // {3=3, 4=4} // console.info(lruCache.get('1')) // null // console.info(lruCache.get('3')) // 3 {4=4, 3=3} // console.info(lruCache.get('4')) // 4 {3=3, 4=4}
- LRU 使用 Map 是基本两个特点
11. 手写一个深拷贝函数,考虑 Map,Set, 循环引用
使用 JSON.stringify 和 parse
- 无法转换函数
- 无法装换 Map Set
- 无法转换循环引用
使用 Object.assign
- 它根本不是深拷贝
普通深拷贝
- 只考虑 Object Array
- 无法转换 Map Set 和循环引用
- 只能应对初级要求的技术一面
答案:
- 考虑 Object Array Map Set
- 考虑循环引用
- 实现ts
/** * 深拷贝 - 只考虑了简单的数组、对象 * @param obj obj */ function cloneDeepSimple(obj: any) { if (typeof obj !== 'object' || obj == null ) return obj let result: any if (obj instanceof Array) { result = [] } else { result = {} } for (let key in obj) { if (obj.hasOwnProperty(key)) { result[key] = cloneDeep(obj[key]) // 递归调用 } } return result } // 功能测试 const a: any = { set: new Set([10, 20, 30]), map: new Map([['x', 10], ['y', 20]]) } a.self = a console.log( cloneDeepSimple(a) ) // 无法处理 Map Set 和循环引用 /** * 深拷贝 * @param obj obj * @param map weakmap 为了避免循环引用 */ export function cloneDeep(obj: any, map = new WeakMap()): any { if (typeof obj !== 'object' || obj == null ) return obj // 避免循环引用 const objFromMap = map.get(obj) if (objFromMap) return objFromMap let target: any = {} map.set(obj, target) // Map if (obj instanceof Map) { target = new Map() obj.forEach((v, k) => { const v1 = cloneDeep(v, map) const k1 = cloneDeep(k, map) target.set(k1, v1) }) } // Set if (obj instanceof Set) { target = new Set() obj.forEach(v => { const v1 = cloneDeep(v, map) target.add(v1) }) } // Array if (obj instanceof Array) { target = obj.map(item => cloneDeep(item, map)) } // Object for (const key in obj) { const val = obj[key] const val1 = cloneDeep(val, map) target[key] = val1 } return target } // 功能测试 const b: any = { set: new Set([10, 20, 30]), map: new Map([['x', 10], ['y', 20]]), info: { city: '北京' }, fn: () => { console.info(100) } } a.self = a console.log( cloneDeep(b) )