一、前端知识深度-原理和源码
1. JS 内存泄漏如何检测?场景有哪些?
什么是垃圾回收
html<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>gc</title> </head> <body> <p> Garbage collection </p> <script> function fn1() { const a = 'aa' console.log(a) const obj = { x: 100} console.log(obj) } // 执行完该函数,函数中的变量会被回收 fn1() function fn2() { const obj = { x: 100 } // 回收不了,这是用户期望的 window.obj = obj; } fn2() function getDataFns() { const data = {}; // 闭包的数据永远都是常驻内存的 return { get(key) { return data[key] }, set(key, value) { data[key] = value } } } const { get, set } = getDataFns(); set('x', 100); get('x'); // 对象被 a 引用 let a = { x: 100 }; let a1 = a; a = 10; a1 = null; // 引用计数缺陷:循环引用 function fn3() { const obj1 = {}; const obj2 = {}; obj1.a = obj2; obj2.a = obj1; } fn3() // JS 根 window 遍历属性 </script> </body> </html>JS 垃圾回收的算法
- 引用计数(之前)js
// 对象被 a 引用 let a = { x: 100 }; let a1 = a; a = 10; a1 = null; - 标记清除(现代)js
// JS 根 window 遍历属性
- 引用计数(之前)
闭包是内存泄漏吗?
- 闭包严格意义上不算内存泄漏
如何检测泄漏
- 使用 Chrome devTools 的 Performance 和 Memory 工具检测 js 内存
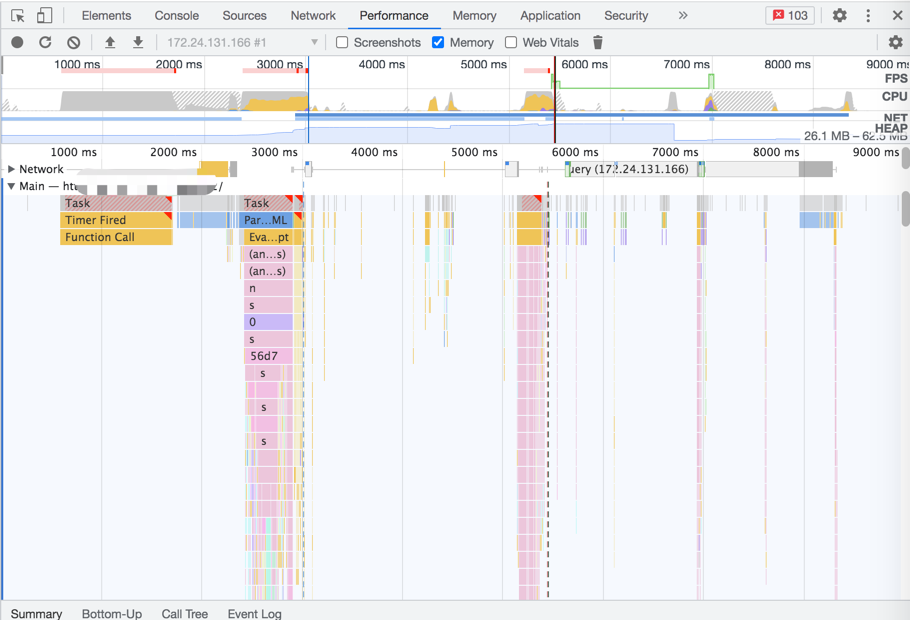
- 扩展:wangEditor 检测内存泄漏
- 内存泄漏的场景(Vue 为例)
被全局变量、函数引用,组件销毁时未清除
vue<template> </template> <script> export default { name: 'MemoryLeak', data() { return { arr: [10, 20, 30] } }, mounted() { window.arr = this.arr; window.printArr = () => { console.log(this.arr) } }, beforeUnmount() { window.arr = null; window.printArr = null }, methods: { } } </script> <style scoped lang='less'> </style>被全局事件、定时器引用,组件销毁时未清除
vue<template> </template> <script> export default { name: 'MemoryLeak', data() { return { arr: [10, 20, 30], // 数组、对象 intervalId: 0 } }, mounted() { this.intervalId = setInterval(() => { console.log(this.arr) }, 100) }, beforeUnmount() { if (this.intervalId) { clearInterval(this.intervalId) } } } </script> <style scoped lang='less'> </style>vue<template> </template> <script> export default { name: 'MemoryLeak', data() { return { arr: [10, 20, 30], // 数组、对象 } }, mounted() { window.addEventListener('resize', this.printArr) }, beforeUnmount() { window.removeEventListener('resize', this.printArr) }, methods: { printArr() { console.log(this.arr) } } } </script> <style scoped lang='less'> </style>被自定义事件引用,组件销毁时未清除
- 使用 eventBus 的时候,on 绑定事件,需要在组件销毁的生命周期函数中使用 off 进行解绑。
- 扩展 WeakMap WeakSet
- WeakMap 的 key 只能是引用类型
- 使用 Chrome devTools 的 Performance 和 Memory 工具检测 js 内存
2. 浏览器和 node.js 的事件循环有什么区别?
答案:
浏览器和 nodejs 的 event loop 流程基本相同。
nodejs 宏任务和微任务分类型,有优先级 注意:
推荐使用 setImmediate 代替 process.nextTick
nodejs 低版本可能会有不同
单线程和异步
- JS 是单线程的(无论在浏览器还是nodejs)。
- 浏览器中 JS 执行和 DOM 渲染公用一个线程。
- 异步
- 宏任务和微任务
- 宏任务:如 setTimeout setInterval 网络请求。
- 微任务:如 promise async/await。
- 优先执行微任务,再执行宏任务html执行顺序:start-->end--->promise then--->timeout
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>event-loop</title> </head> <body> <p>event-loop</p> <script> console.log('start'); setTimeout(() => { console.log('timeout') }) Promise.resolve().then(() => { console.log('promise then') }) console.log('end') </script> </body> </html>
- 优先执行微任务,再执行宏任务
- 微任务在下一轮 DOM 渲染之前执行,宏任务在之后执行。html
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>event-loop</title> </head> <body> <p>event-loop</p> <script> const p = document.createElement('p'); p.innerHTML = 'new paragraph'; document.body.appendChild(p); const ps = document.getElementsByTagName('p'); console.log('ps--->', ps.length) console.log('start'); // 渲染之前触发 setTimeout(() => { const ps = document.getElementsByTagName('p'); console.log('ps timeout--->', ps.length) alert('阻塞 timeout'); }) // 渲染之后触发 Promise.resolve().then(() => { const ps = document.getElementsByTagName('p'); console.log('ps promise then--->', ps.length) alert('阻塞 promise'); }) console.log('end'); </script> </body> </html>
- 宏任务队列 MarcoTask Queue
- 微任务队列 MircoTask Queue
- nodejs异步
- Nodejs 同样使用 ES 语法,也是单线程,也需要异步。
- 异步任务:宏任务、微任务。
- 但是,它的宏任务和微任务,分不同类型,有不同优先级。
- nodejs 宏任务类型和优先级
- Timers: setTimeout setInterval
- I/O callbacks: 处理网络、流、TCP 的错误回调
- Idle, prepare: 闲置状态(nodejs 内部使用)
- Poll 轮询: 执行 poll 中的 I/O 队列
- Check 检查: 存储 setImmediate 回调
- Close callbacks: 关闭回调,如 socket.on('close')
- nodejs 微任务类型和优先级
- promise async/await process.nextTick
- 注意:process.nextTick 优先级最高js
console.log('start') setImmediate(() => { console.log('setImmediate') }) setTimeout(() => { console.log('setTimeout') }) Promise.resolve().then(() => { console.log('Promise then') }) process.nextTick(() => { console.log('nextTick') }) console.log('end')
- nodejs event loop
- 执行同步代码
- 执行微任务(process.nextTick 优先级最高)
- 按顺序执行 6 个类型的宏任务(每当开始之前都执行当前的微任务)
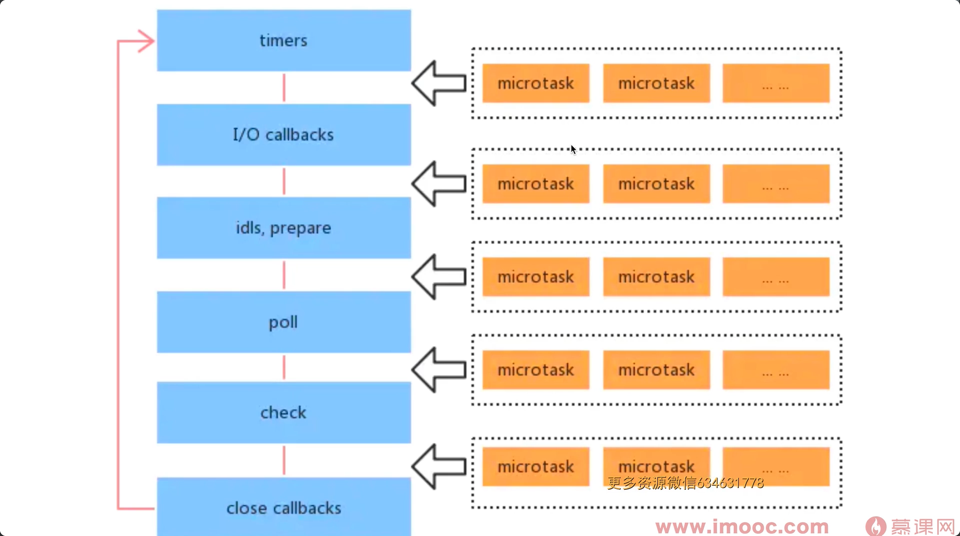
- nodejs 宏任务类型和优先级
- 宏任务和微任务
3. vdom 真的很快吗?
答案:
vdom 并不快, JS 直接操作 DOM 才是最快的
但 "数据驱动视图"要有合适的技术方案,不能全部 DOM 重建
vdom 就是目前最合适的技术方案(并不是因为它快,而是合适)
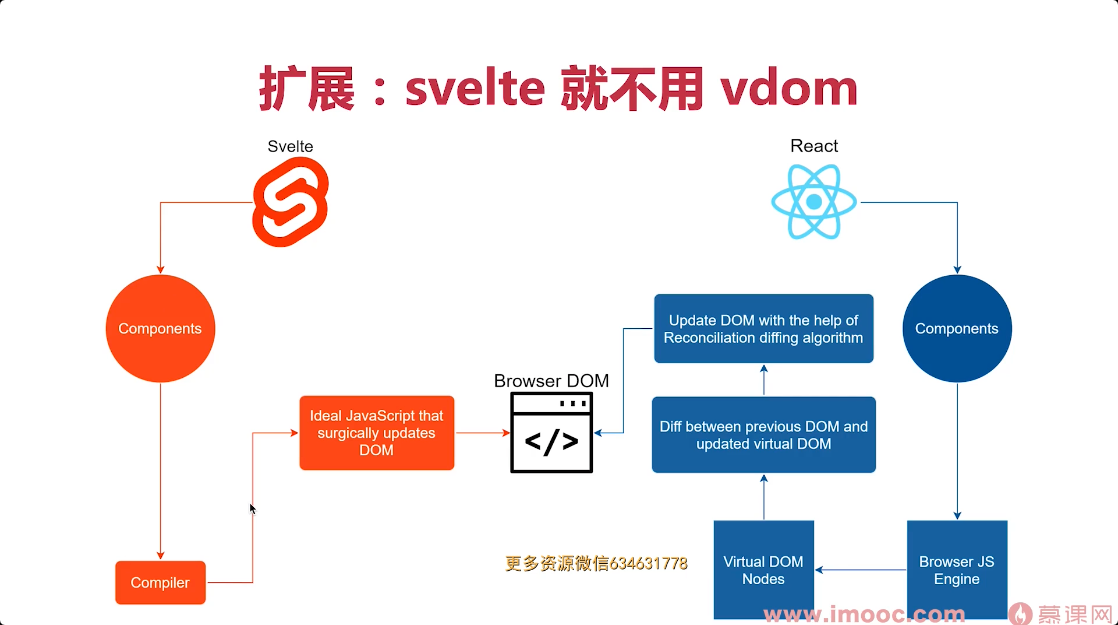
vdom
- Virtual DOM, 虚拟 DOM
- 用 JS 对象模拟 DOM 节点数据
- 由 React 最新推广使用
Vue React 等框架的价值
- 组件化
- 数据视图分离,数据驱动视图(核心)
- 只关心业务数据,而不用再关心 DOM 变化
数据驱动视图,技术方案:vdom
- data 变化
- diff 算法 vnode oldVnode
- 更新 DOM
扩展:svelte 就不用 vdom
4. 遍历数组,for 和 forEach 哪个快?
答案:
- for 更快
- forEach 每次都要创建一个函数来调用,而 for 不会创建函数
- 函数需要独立的作用域,会有额外的开销html
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>for-foreach</title> </head> <body> <script> const arr = []; for (let i = 0; i < 100 * 10000; i++) { arr.push(i) } const length = arr.length console.time('for') let n1 = 0; for (let i = 0; i < length; i++) { n1++ } console.timeEnd('for') // 3.7ms console.time('forEach') let n2 = 0; arr.forEach(() => n2++) console.timeEnd('forEach') // 15.1ms </script> </body> </html>
5. Node.js 如何开启进程,进程如何通讯?
答案:
- 开启子进程 child_process.fork 和 cluster.fork
- 使用 send 和 on 传递消息
涉及相关知识点:
进程 process vs 线程 thread
- 进程,OS 进行资源分配和调度的最小单位,有独立内存空间。
- 线程,OS 进行运算调度的最小单位,共享进程内存空间。
- JS 是单线程的,但可以开启多线程执行,如 WebWorker
为何需要多进程?
- 多核 CPU,更适合处理多进程
- 内存较大,多个进程才能更好的利用(单进程有内存上限)
- 总之,"压榨"机器资源,更快,更节省
代码演示
- node 进程js
const http = require('http'); const server = http.createServer(); server.listen(3000, () => { console.log('localhost: 3000') }) console.info(process.pid) - node child_process.forkjs
const http = require('http'); const fork = require('child_process').fork const server = http.createServer((req, res) => { if (req.url === '/get-sum') { console.info('主进程 id', process.pid) // 开启子进程 const computeProcess = fork('./compute.js'); computeProcess.send('开始计算'); computeProcess.on('message', data => { console.info('主进程接受到的信息:', data) res.end('sum is' + data) }) computeProcess.on('close', () => { console.info('子进程因报错而退出'); computeProcess.kill(); res.end('error') }) } }); server.listen(3000, () => { console.info('localhost: 3000') }) - node cluster.forkjs
const http = require('http'); const cpuCoreLength = require('os').cpus().length; const cluster = require('cluster'); if (cluster.isPrimary) { for (let i = 0; i < cpuCoreLength; i++) { cluster.fork(); // 开启子进程 } cluster.on('exit', worker => { console.log('子进程退出') cluster.fork(); // 进程守护 }) } else { // 多个子进程会共享一个 TCP 连接,提供一个网络服务 const server = http.createServer((req, res) => { res.writeHead(200); res.end('done'); }); server.listen(3000) } // 工作中 进程守护 使用 PM2
- node 进程
重点:
- 进程 VS 线程
- JS 是单线程的
- 为何需要多进程?
6. 请描述 JS Bridge 原理
什么是JS Bridge
- JS 无法直接调用 native API
- 需要通过一些特定的"格式"来调用
- 这些"格式"就统称 JS Bridge,例如微信JS-SDK
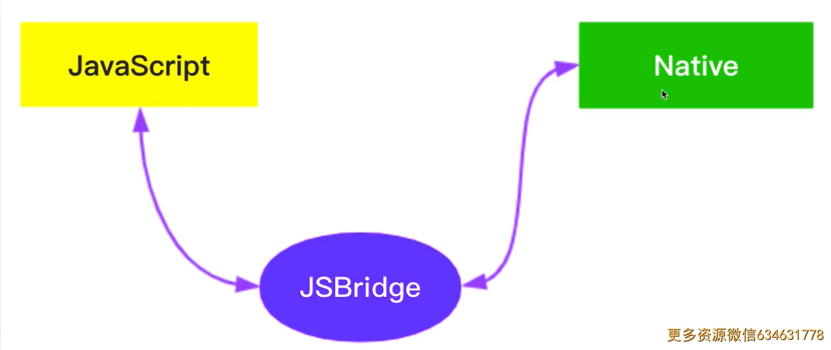
JS Bridge 的常见实现方式
- 注册全局 API
- URL Scheme
- 代码演示html
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>js-bridge</title> </head> <body> <p>js-bridge</p> <iframe id="iframe1"></iframe> <script> // 全局注册 // const version = window.getVersion() // URL Scheme 通过自定义协议来提供相应的能力 异步 // 简单用法 const iframe1 = document.getElementById('iframe1'); iframe1.onload = () => { const content = iframe1.contentWindow.document.body.innerHTML; } iframe1.src = 'my-app-name://api/getVersion' // 封装 JS-Bridge const sdk = { invoke(url, data = {}, onSuccess, onError) { const iframe = document.createElement('iframe'); iframe.style.visibility = 'hidden'; document.body.appendChild(iframe); iframe.onload = () => { const content = iframe.contentWindow.document.body.innerHTML; onSuccess(JSON.parse(content)); iframe.remove(); } iframe.onerror = () => { onError(); iframe.remove(); } iframe.src = `my-app-name://${url}?data=${JSON.stringify(data)}` }, fn1(data, onSuccess, onError) { sdk.invoke('api/fn1', data, onSuccess, onError) }, fn2(data, onSuccess, onError) { sdk.invoke('api/fn2', data, onSuccess, onError) } } sdk.fn1() </script> </body> </html>
7. 是否了解过 requestIdleCallback? 和 requestAnimationFrame 有什么区别?
答案:
requestAnimationFrame 每次渲染完都会执行,高优
requestIdleCallback 空闲时才执行,低优
由 React fiber 引起的关注
- 组件树转换为链表,可分段渲染
- 渲染时可以暂停,去执行其他高优任务,空闲时再继续渲染
- 如何判断空闲?
- requestIdleCallback
代码
html<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>requestAnimationFrame</title> </head> <body> <p>requestAnimationFrame</p> <button id="btn">change</button> <div id="box"></div> <script> const box = document.getElementById('btn'); document.getElementById('btn').addEventListener('click', () => { let curWidth = 100; const maxWidth = 400; function addWidth() { curWidth = curWidth + 3; box.style.width = `${curWidth}px` if (curWidth < maxWidth) { // window.requestAnimationFrame(addWidth); window.requestIdleCallback(addWidth); } } addWidth() }) </script> </body> </html>他们是宏任务还是微任务
- 两者都是宏任务
- 要等待 DOM 渲染完成之后才执行,肯定是宏任务。html
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>requestIdleCallback</title> </head> <body> <script> // 顺序:start end setTimeout requestAnimationFrame requestIdleCallback window.onload = () => { console.log('start') setTimeout(() => { console.log('setTimeout') }) window.requestAnimationFrame(() => { console.log('requestAnimationFrame') }) window.requestIdleCallback(() => { console.log('requestIdleCallback') }) console.log('end') } </script> </body> </html>
8. Vue 每个生命周期都做了什么?
重点
- Vue 生命周期必须掌握
- 连环问:Vue 什么时候操作 DOM 比较合适
- mounted 和 updated 都不能保证子组件全部挂载完成
- 使用 $nextTick 渲染 DOMvue
<template> </template> <script> export default { name: "NextTick", mounted() { this.$nextTick(function () { // 仅在整个视图都被渲染之后才会运行的代码 }) } } </script> <style scoped> </style>
- 连环问:Ajax 应该在哪个生命周期?
- 有两个选择:created 和 mounted
- 推荐:mounted
- 连环问:Vue3 Composition API 生命周期有何区别?
- 用 setup 代替了 beforeCreate 和 created
- 使用 Hooks 函数的形式,如 mounted 改为 onMounted()
beforeCreate
- 创建一个空白的 Vue 实例
- data method 尚未被初始化,不可使用
created
- Vue 实例初始化完成,完成响应式绑定。
- data method 都已经初始化完成,可调用。
- 尚未开始渲染模板
beforeMount
- 编译模板,调用 render 生成 vdom
- 还没有开始渲染 DOM
mounted
- 完成 DOM 渲染
- 组件创建完成
- 开始由 "创建阶段" 进入 "运行阶段"
beforeUpdate
- data 发生变化之后
- 准备更新 DOM(尚未更新 DOM)
updated
- data 发生变化,且 DOM 更新完成
- (不要在 updated 中修改 data, 可能会导致死循环)
beforeUnmount
- 组件进入销毁阶段(尚未销毁,可正常使用)
- 可移除、解绑一些全局事件、自定义事件
unmounted
- 组件被销毁了
- 所有子组件也都被销毁了
keep-alive 组件
- onActivated 缓存组件被激活
- onDeactivated 缓存组件被隐藏
9. Vue2 Vue3 React 三者 diff 算法有何区别?
介绍 diff 算法
- diff 算法很早就有。
- diff 算法应用广泛,例如 github 的 Pull Request 中的代码 diff。
- 如果要严格 diff 两棵树,时间复杂度 O(n^3) 不可用。
diff 算法 优化 O(n)
- 只比较同一层级,不跨级比较
- tag 不同则删掉重建(不再去比较内部的细节)
- 子节点通过 key 区分(key 的重要性)
React diff 仅右移
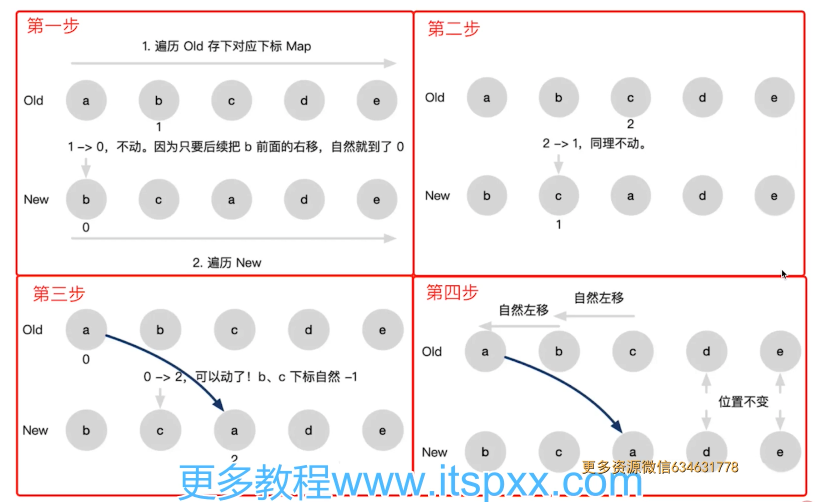
Vue2 diff 双端比较
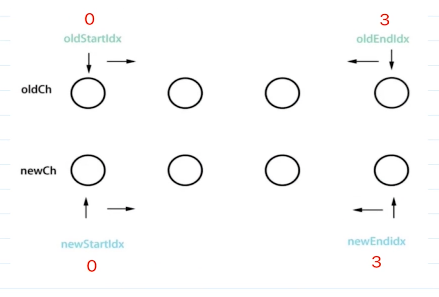
Vue3 diff 最长递增子序列
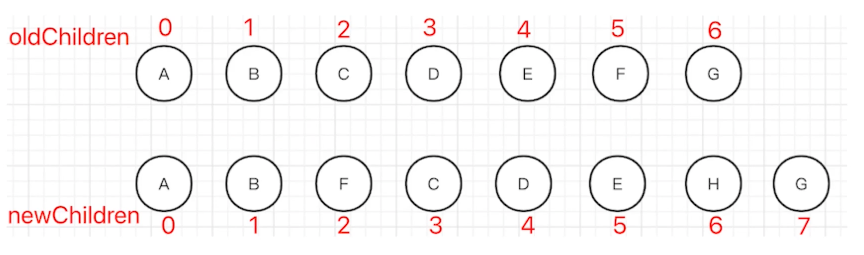
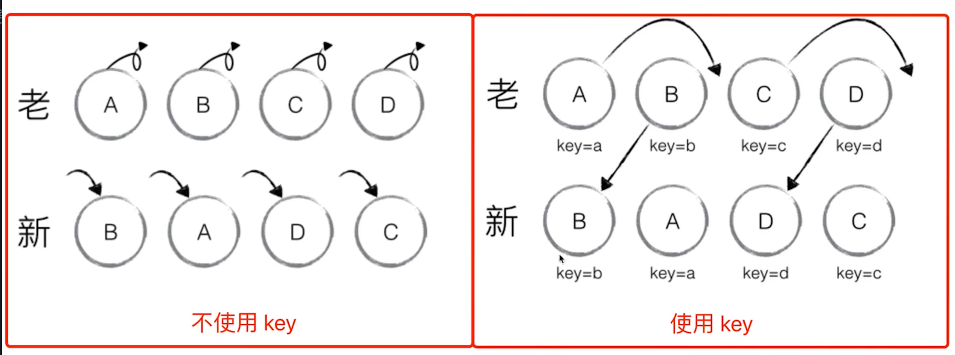
连环问:Vue React 为何循环时必须使用 key?
- vdom diff 算法会根据 key 判断元素是否删除?
- 匹配了 key,则只移动元素-性能较好
- 未匹配 key,则删除重建-性能较差
10. Vue-router MemoryHistory(abstract)
Vue-router 三种模式
- Hash
- WebHistory
- MemoryHistory(V4 之前叫做 abstract history)
代码
createWebHistory 的实现方式
- history.pushState
- window.onpopstate
createWebHashHistory 的实现方式
- location.hash
createMemoryHistory 的实现方式
- 不可前进、后退
- 只在一个页面中进行路由的切换